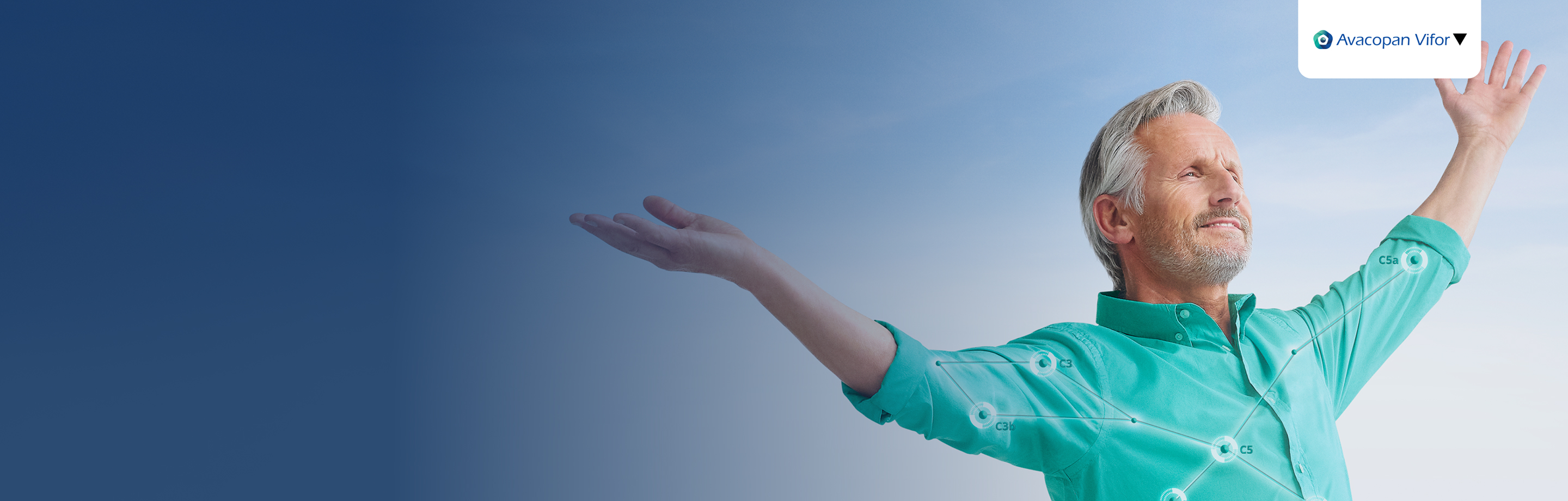
Avacopan Vifor▼
Learn more about Avacopan Vifor for the treatment of severe, active GPA/MPA in eligible adult patients1
Click here for Prescribing Information
Avacopan Vifor▼
Learn more about Avacopan Vifor for the treatment of severe, active GPA/MPA in eligible adult patients1
Click here for Prescribing Information
Avacopan Vifor▼
Learn more about Avacopan Vifor for the treatment of severe, active GPA/MPA in eligible adult patients1
Click here for Prescribing InformationAvacopan Vifor with a cyclophosphamide or rituximab regimen, is recommended by NICE, within its marketing authorisation, as an option for treating severe, active granulomatosis with polyangiitis (GPA) or microscopic polyangiitis (MPA) in adults1,2
Menu
Efficacy
Efficacy
The ADVOCATE Study

The efficacy and safety of Avacopan Vifor was evaluated in the ADVOCATE trial, an international, multicentre, active‑comparator, randomised, double-blind, double-dummy, controlled, pivotal phase 3 trial of 52 weeks duration3*

Adapted from: Jayne D, et al. N Engl J Med, 2021
Key inclusion/exclusion criteria3,4
Key inclusion/exclusion criteria3,4
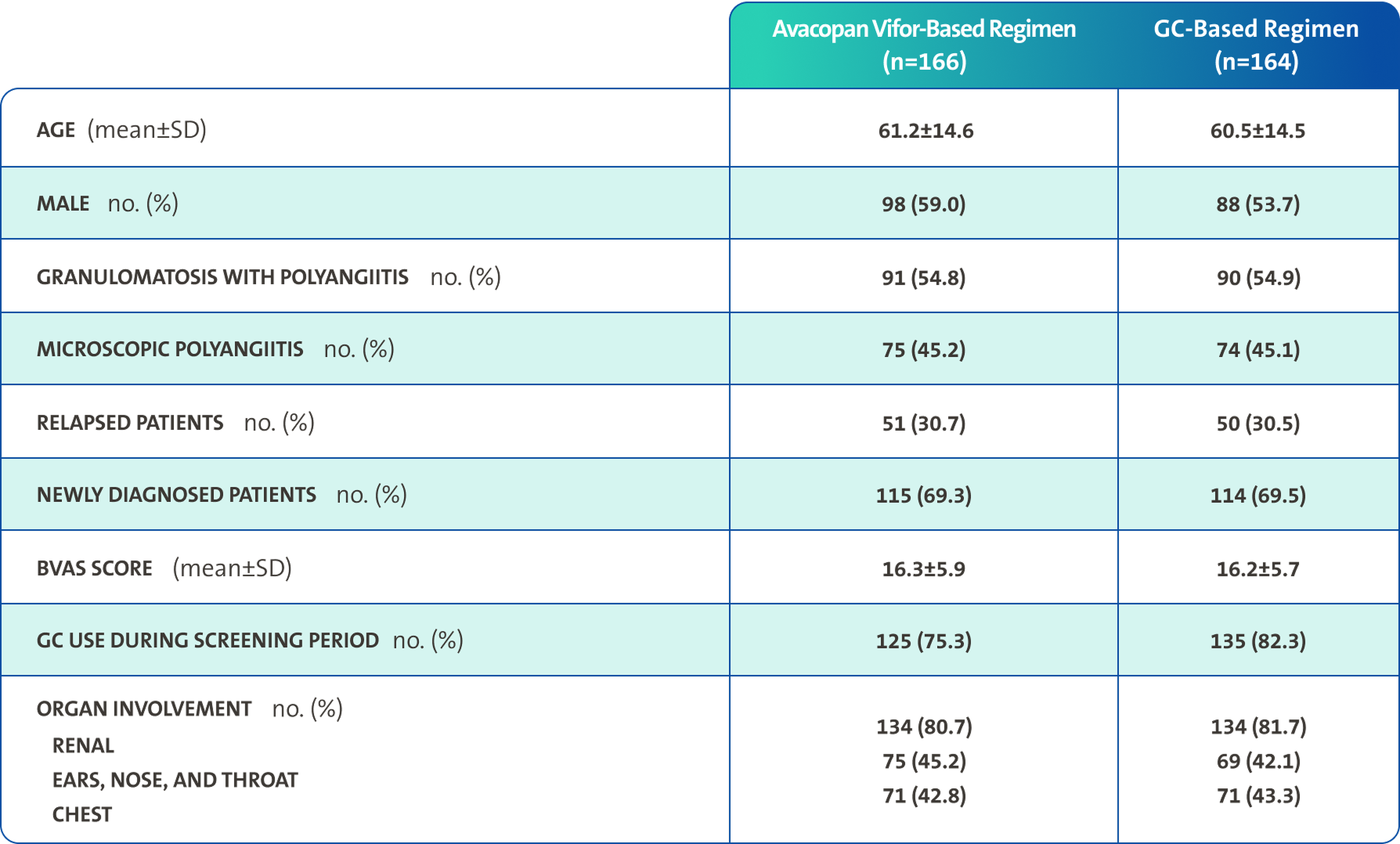
Baseline characteristics3
Baseline characteristics3
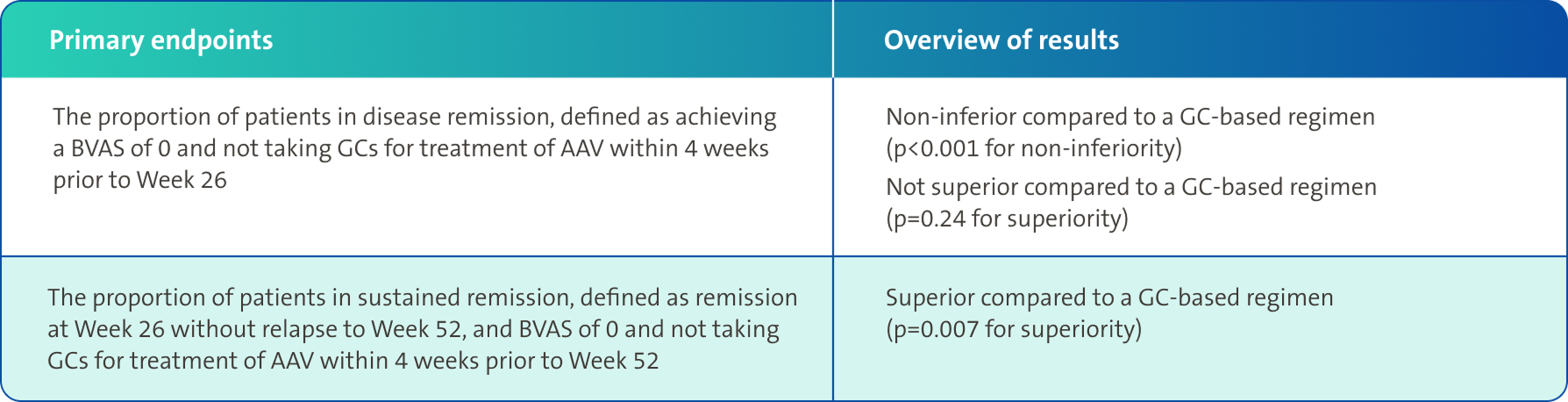
Primary endpoints3
Primary endpoints3
Secondary endpoints3,4
Secondary endpoints3,4

There was no pre-specified plan for adjustment of confidence intervals for multiplicity of the secondary end points; point estimates and 95% confidence intervals only are presented, and no definite conclusions can be drawn from these data3
*Relapse was defined as occurrence of at least one major item in the BVAS, or three or more minor items in the BVAS, or one or two minor items in the BVAS at two consecutive visits, after having previously achieved remission at Week 26 (BVAS 0 and having received no GCs for treatment of vasculitis for 4 weeks)4
Primary and Secondary Endpoint Results1,3,5

Remission rates3
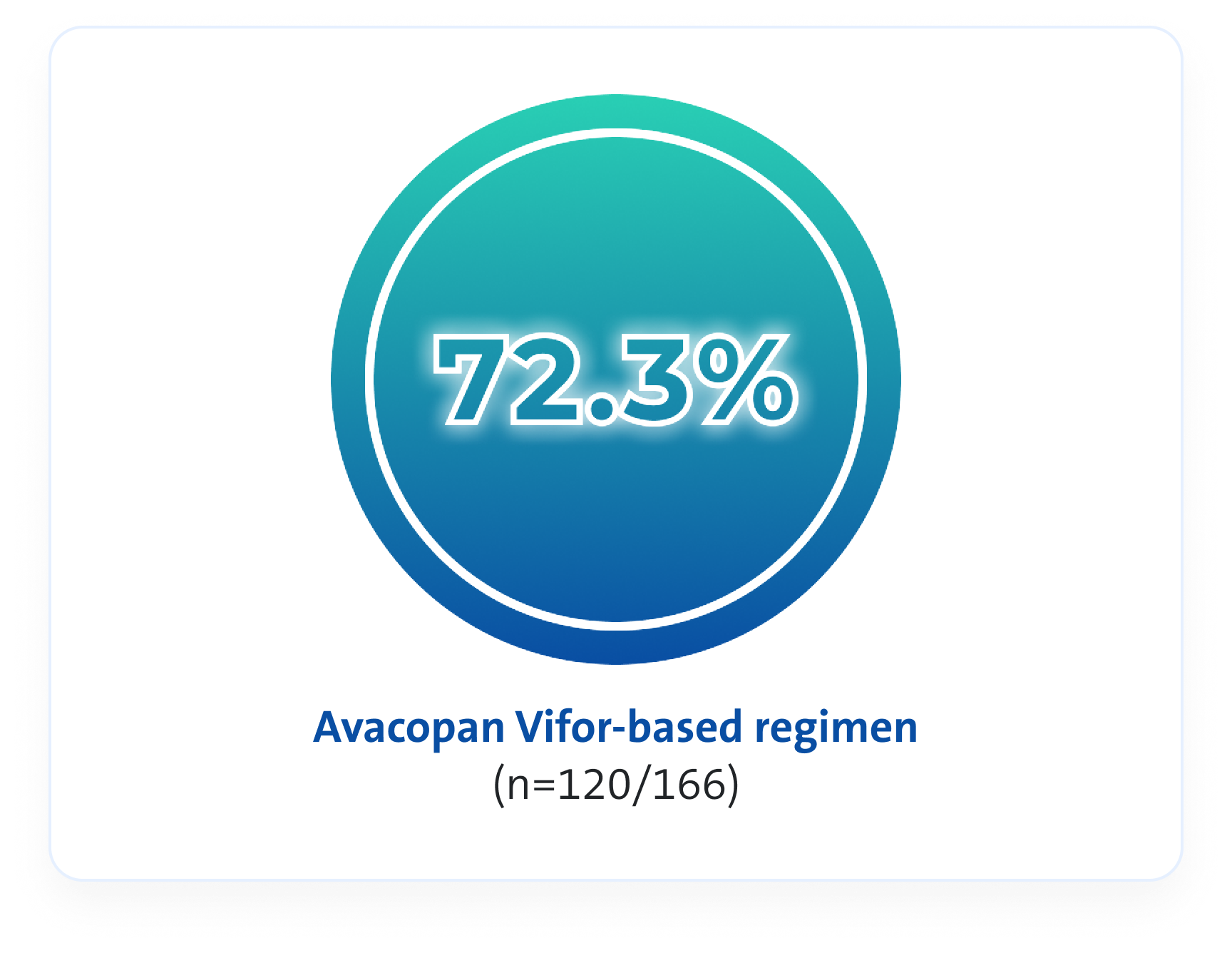
An Avacopan Vifor-based regimen was non-inferior but not superior vs GC-based regimen with respect to remission at Week 26, and superior with respect to sustained remission at Week 523*
At Week 26, an Avacopan Vifor-based regimen demonstrated non-inferiority in achieving clinical remission vs a GC‑based regimen3
p<0.001 for non-inferiority
VS
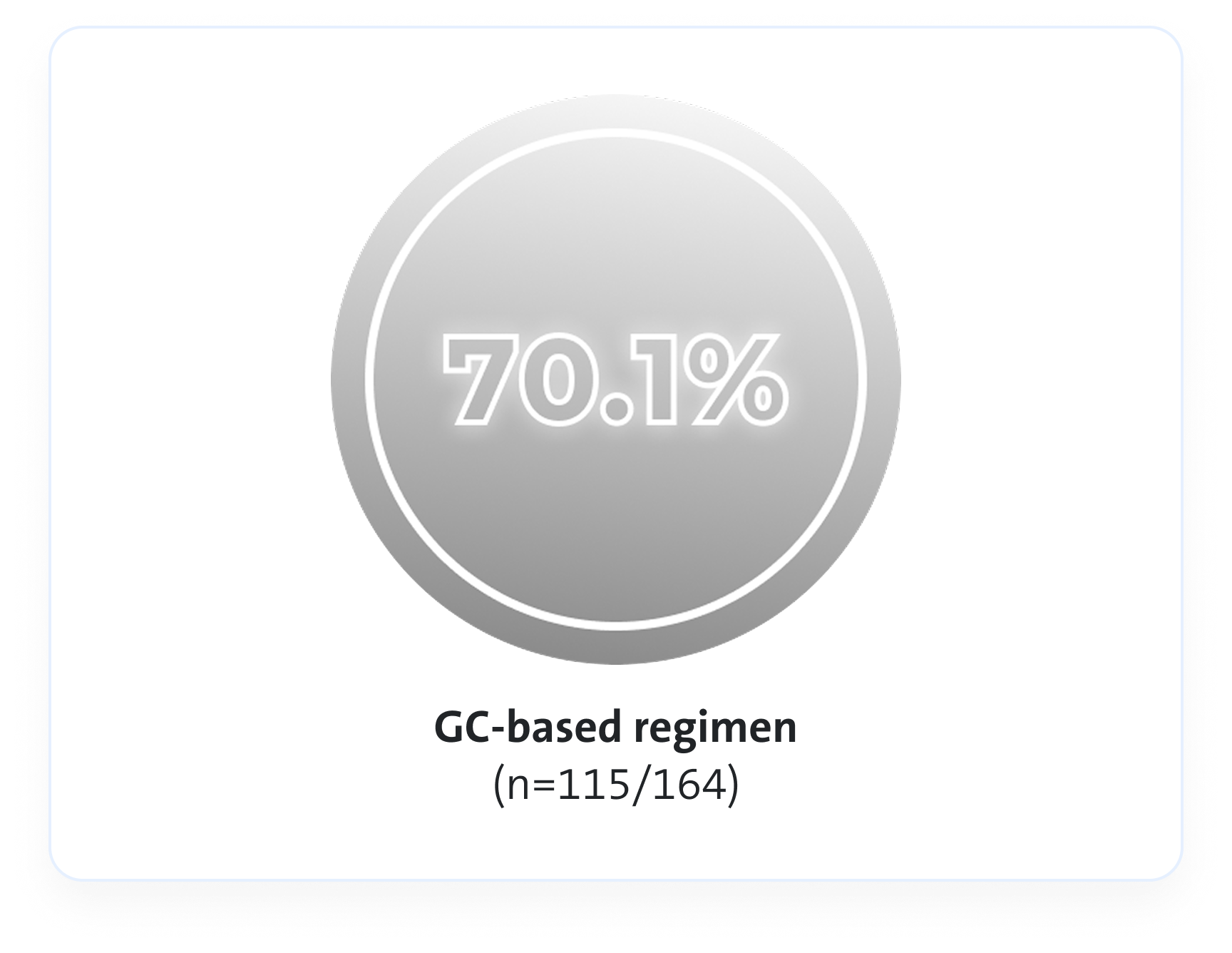
Estimated common difference, 3.4 (95% CI, -6.0 to 12.8)
At Week 52, an Avacopan Vifor-based regimen demonstrated superior sustained clinical remission vs a GC‑based regimen3
p=0.007 for superiority
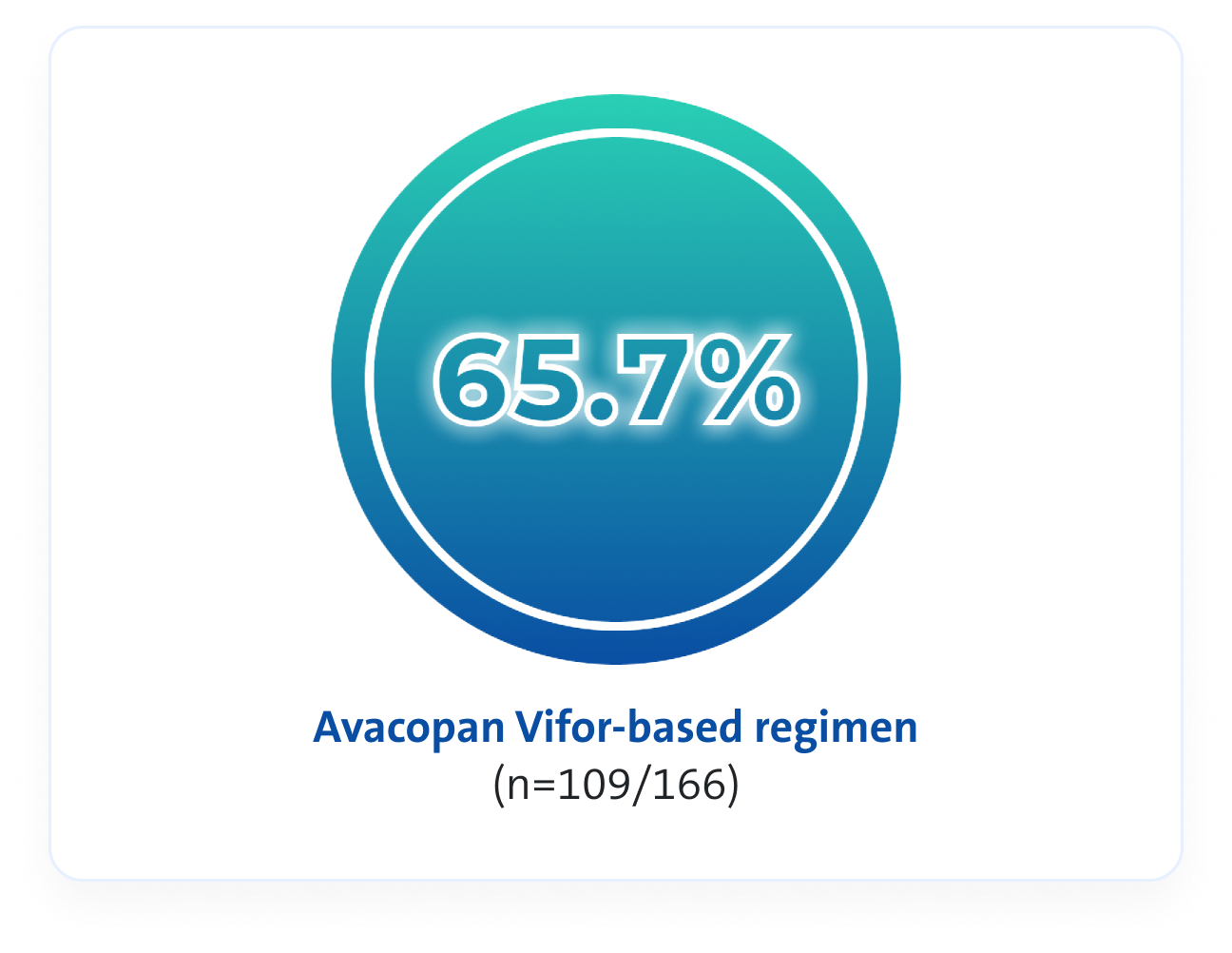
VS
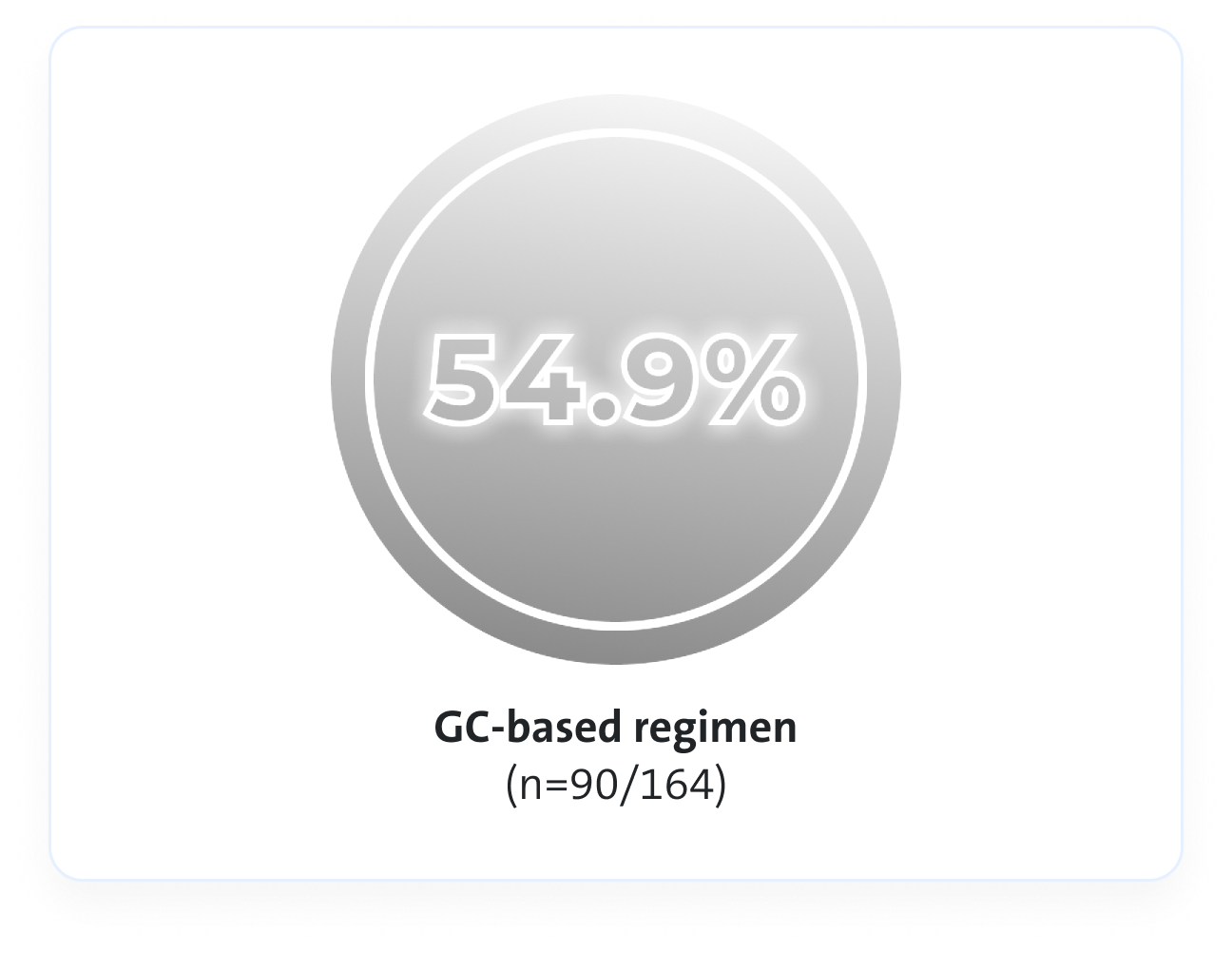
Estimated common difference, 12.5 (95% CI, 2.6 to 22.3)
At Week 52, Avacopan Vifor-based regimen demonstrated a NNT between 8 and 10
*Clinical remission in the ADVOCATE study was defined as BVAS 0 and no GC use in previous 4 weeks3
Renal function - eGFR3
An Avacopan Vifor-based regimen and GC-based regimen demonstrated numerical increases in eGFR, compared to baseline3
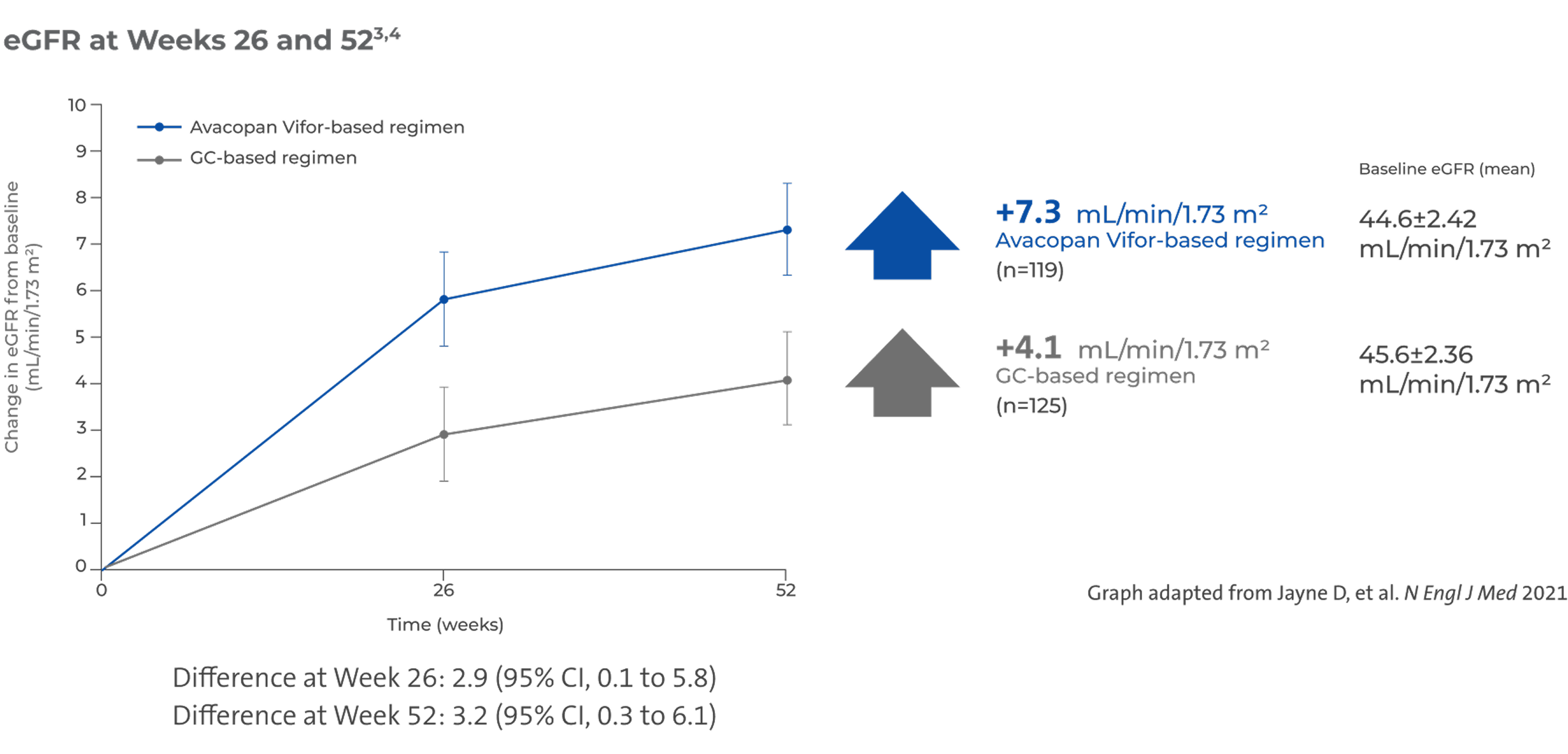
Larger numerical increase in eGFR in patients with Stage 4 chronic kidney disease (CKD)3,4,6
In a subset of patients with baseline eGFR <30 mL/min/1.73 m2 (n=100), there was a larger numerical increase in eGFR, compared to other stages of CKD3,4,6
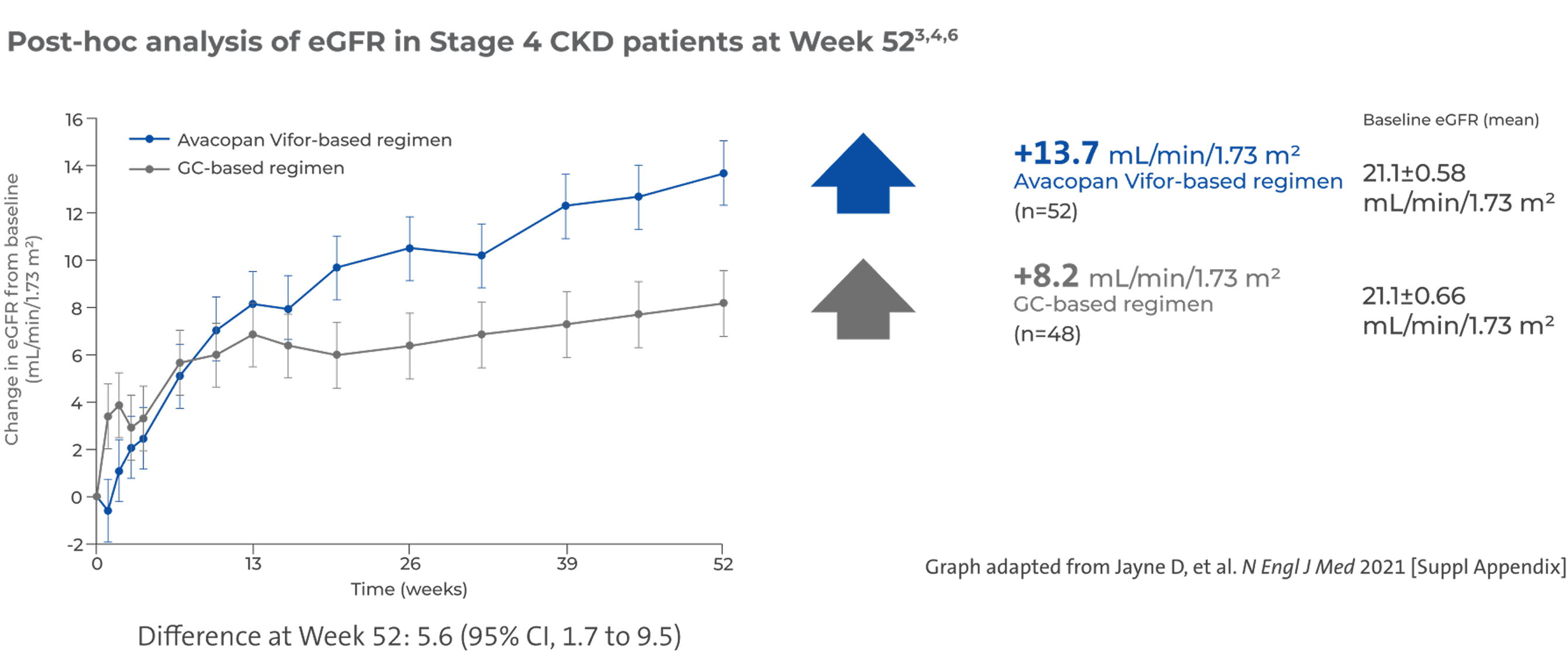
There was no pre-specified plan for adjustment of confidence intervals for multiplicity of the secondary end points; point estimates and 95% confidence intervals only are presented, and no definite conclusions can be drawn from these data3
Renal function - UACR & MCP-13,4
An Avacopan Vifor-based regimen demonstrated rapid improvement in albuminuria at Week 4 and numerically similar change at Week 52 across the treatment groups3,4
Reduction in UACR at Week 43

VS
(Difference, -40, 95% Cl, -53 to -22)3
Numerically similar change in UACR was observed across the treatment groups at week 52: -74% in Avacopan Vifor‑based arm (n=109) vs -77% in GC-based arm (n=114) (Difference 12, 95% Cl, -14 to 45)3
An Avacopan Vifor-based regimen demonstrated a reduction in urinary inflammation compared to baseline4
Reduction in inflammation at Week 134

VS
59% decrease in urinary MCP-1:creatinine ratio in Avacopan Vifor-based regimen (n=113) vs 52% decrease in GC-based regimen (n=120)2 (Difference -15, 95% Cl, -28 to -1)4
There was no pre-specified plan for adjustment of confidence intervals for multiplicity of the secondary endpoints; point estimates and 95% confidence intervals only are presented, and no definite conclusions can be drawn from these data3
Relapse risk3
Avacopan Vifor based regimen resulted in a lower absolute risk of relapse vs a GC-based regimen over 52 weeks3
Avacopan Vifor-based regimen demonstrated a 54% relative risk reduction in relapse vs a GC-based regimen over 52 weeks3
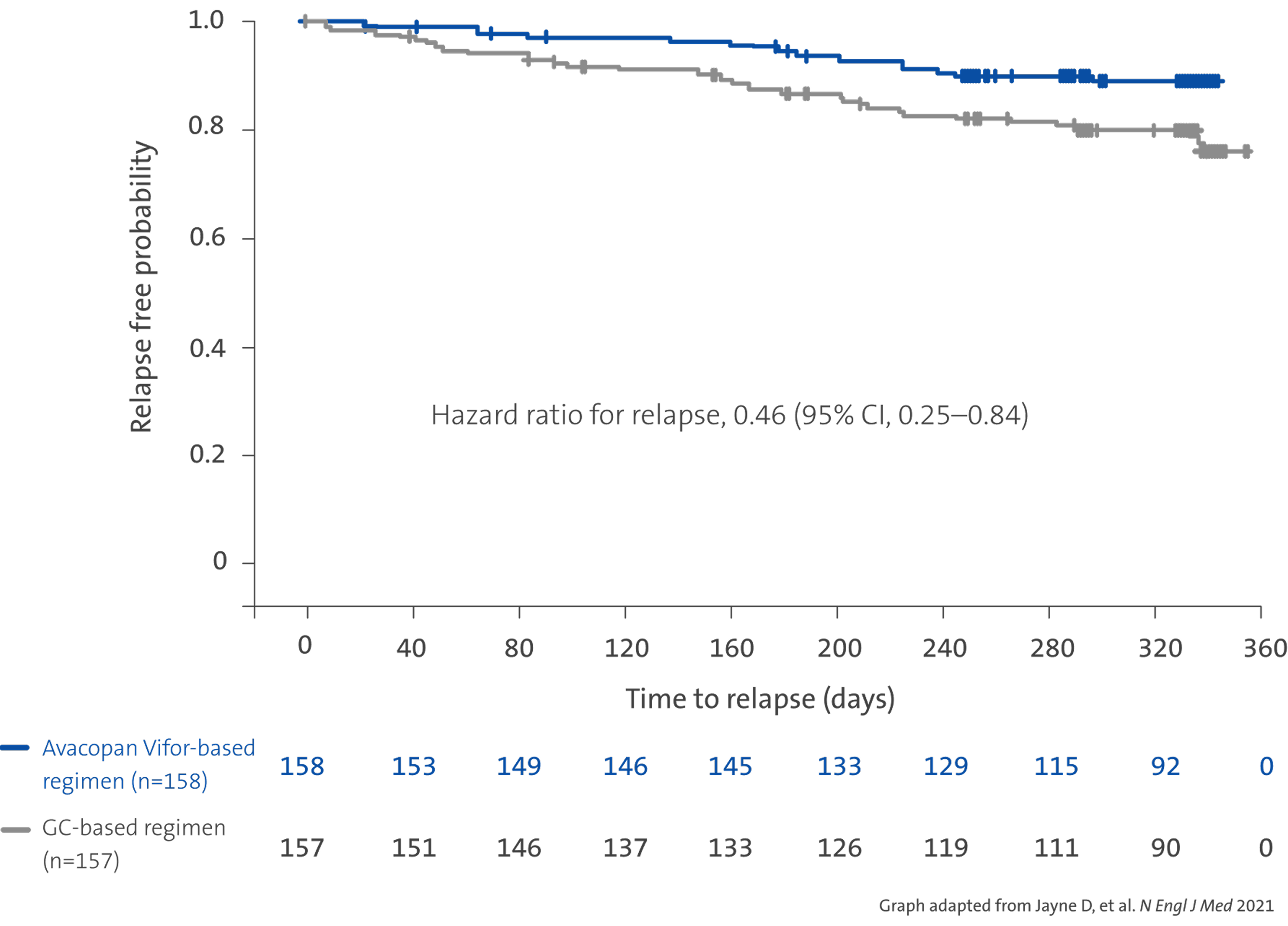
Absolute risk of relapse over 52 weeks of treatment3
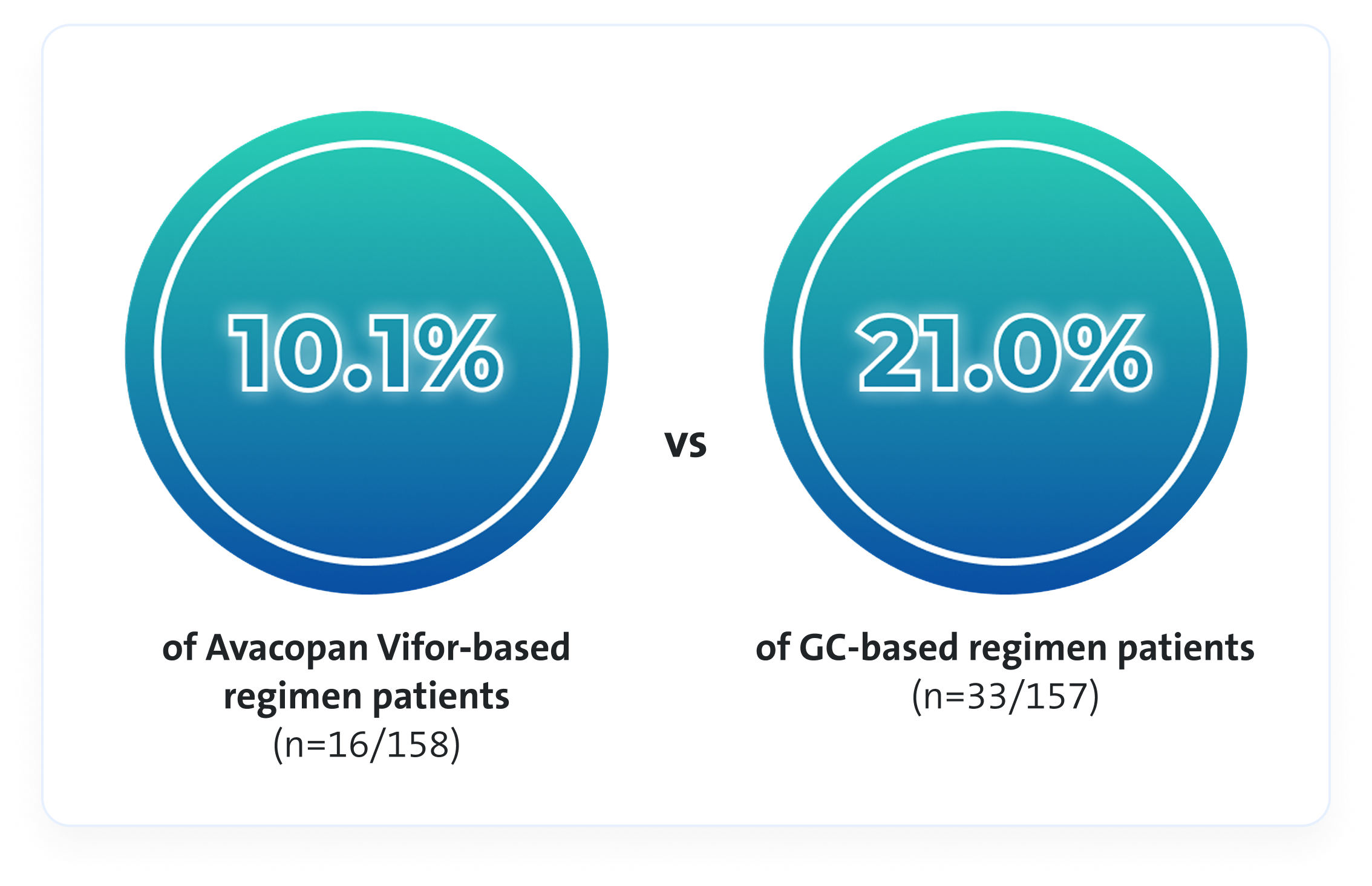

There was no pre-specified plan for adjustment of confidence intervals for multiplicity of the secondary endpoints; point estimates and 95% confidence intervals only are presented, and no definite conclusions can be drawn from these data3
GC toxicity3,7
Avacopan Vifor-based regimen demonstrated a larger reduction in GC-toxicity vs a GC‑based regimen3
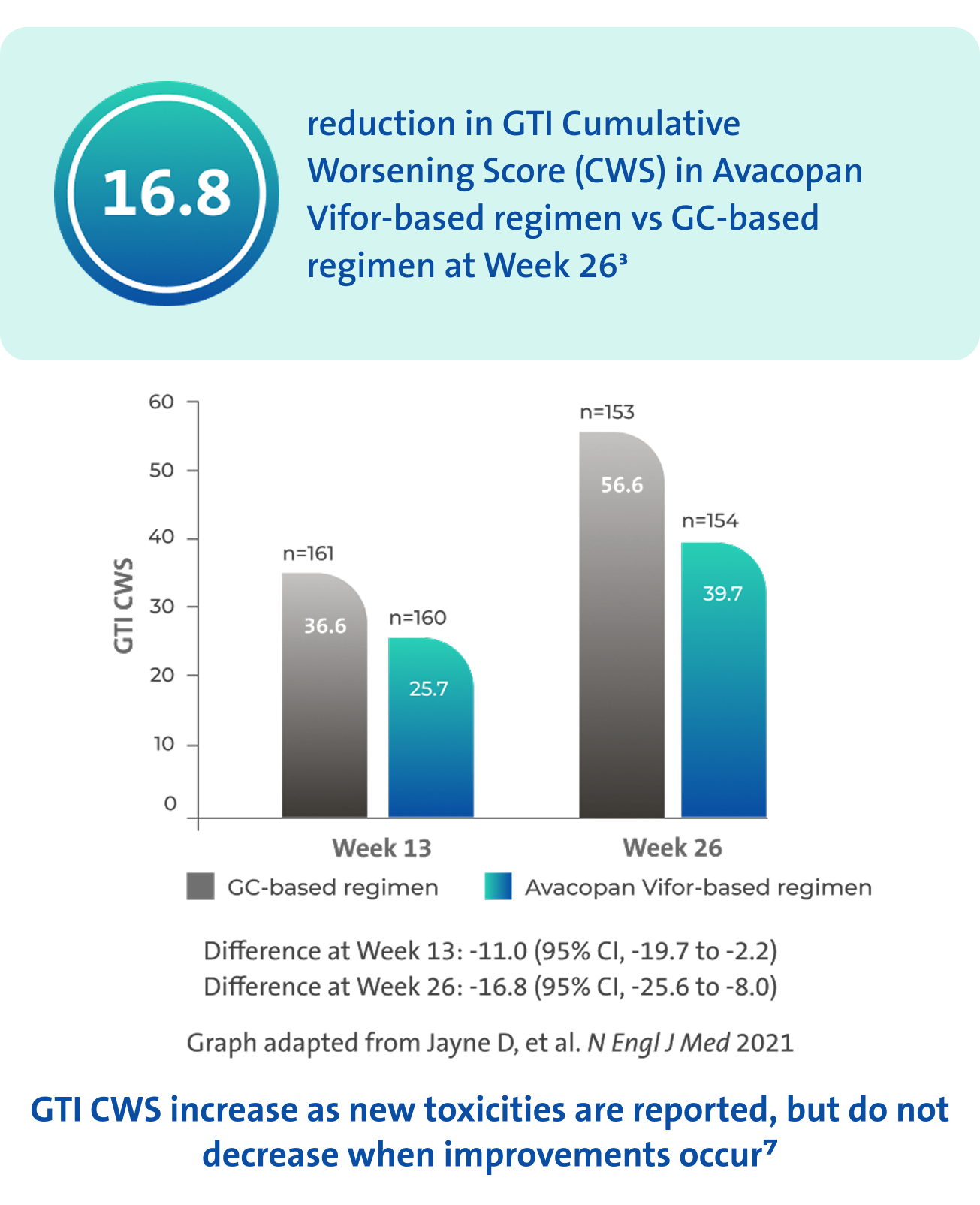
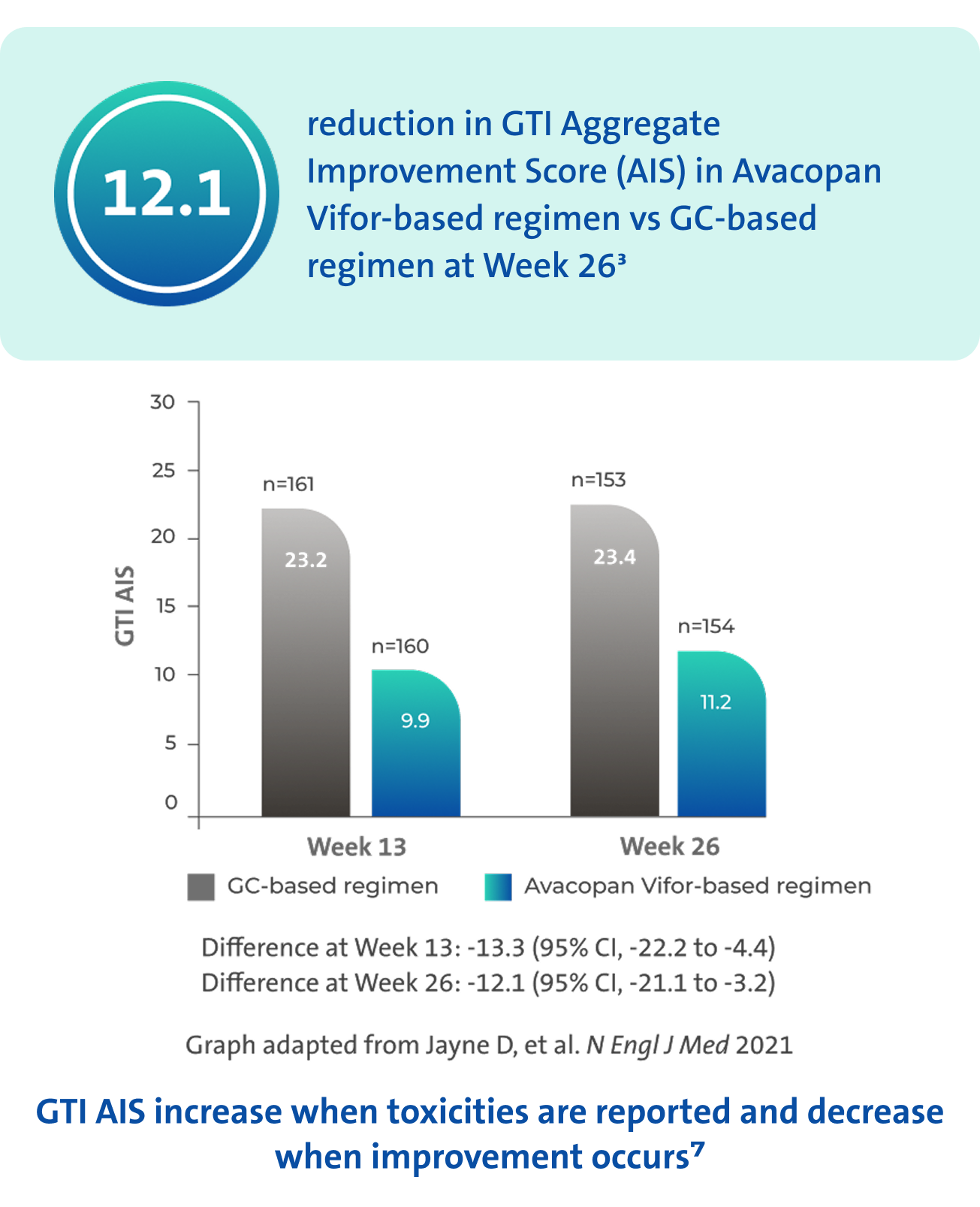
There was no pre-specified plan for adjustment of confidence intervals for multiplicity of the secondary endpoints; point estimates and 95% confidence intervals only are presented, and no definite conclusions can be drawn from these data3
GC use1,4,8
In the ADVOCATE trial an Avacopan Vifor-based regimen allowed physicians to use less GCs compared to GC-based regimen1,4,8
In the trial GCs were given as follows:4
- Study supplied GC: 60 mg/day oral prednisone, tapered over 20 weeks for those randomised to the GC‑based regimen
- Non-study supplied GC: Various forms and doses of GCs were administered to patients in both arms of the study, for both GPA/MPA-related reasons and for unrelated reasons
For analysis purposes, all forms of GCs were converted to a prednisone-equivalent dose to allow calculation of the total GC dose administered throughout the study4
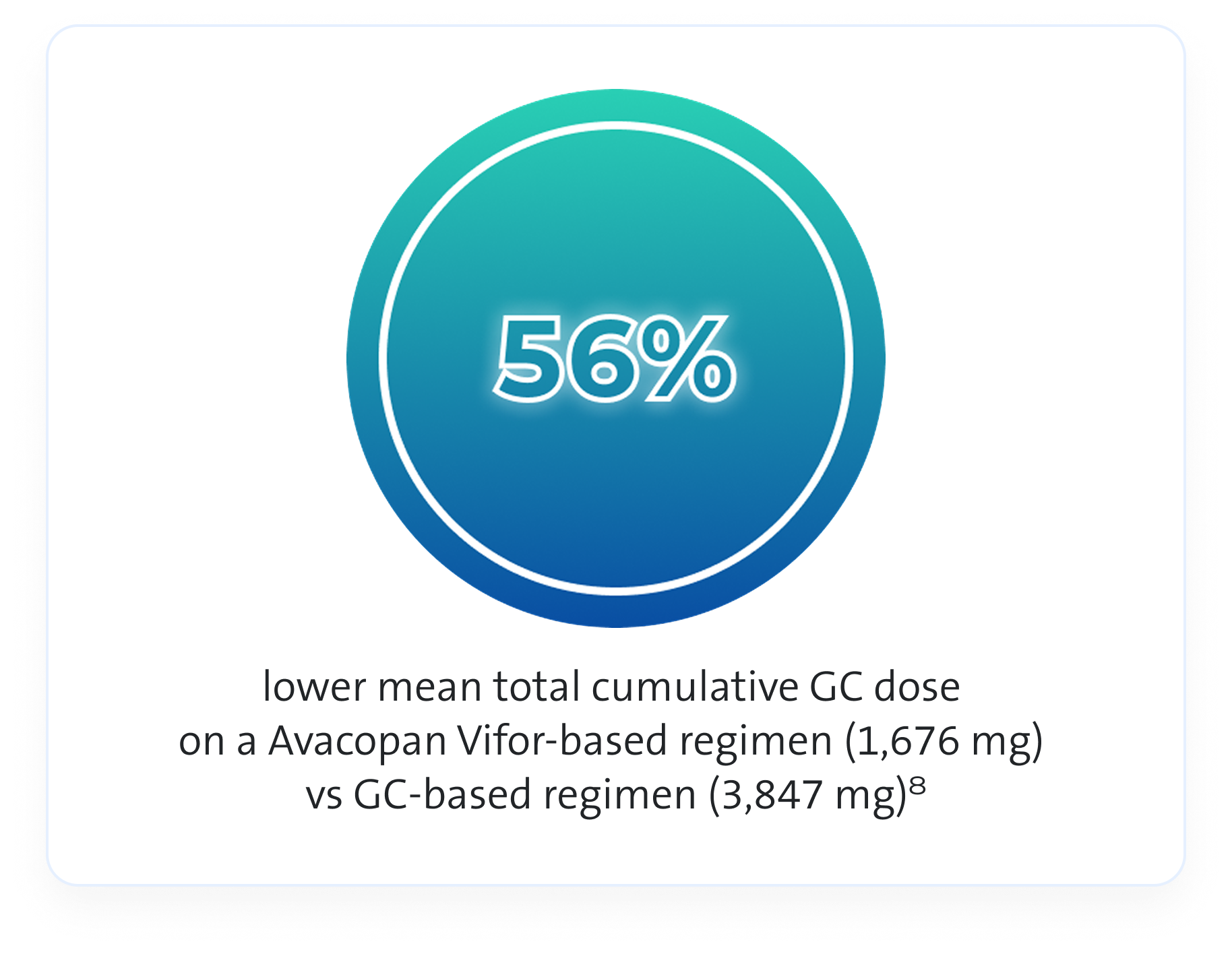
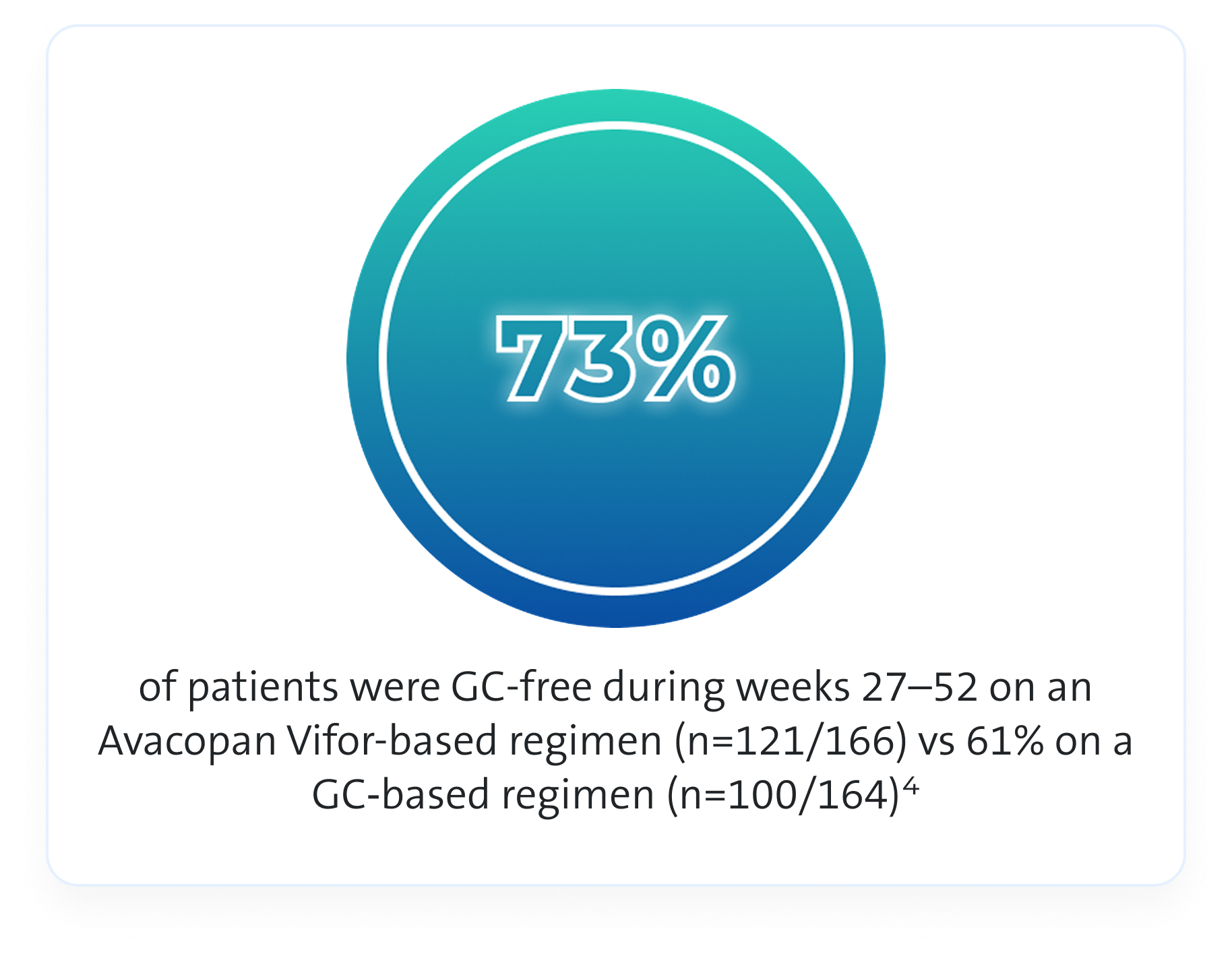
As this is observational data, no definite conclusions can be drawn
References & footnotes
Footnotes
*All the patients received one of three regimens: CYC IV at a dose of 15 mg/kg of body weight up to 1.2 g on Day 1 and at Weeks 2, 4, 7, 10, and 13; CYC orally at a dose of 2 mg/kg up to 200 mg/day for 14 weeks; or IV RTX at a dose of 375 mg/m2 body-surface area/week for 4 weeks. From Week 15 onward, CYC was followed by oral AZA at a target dose of 2 mg/kg/day. No RTX was given beyond the first 4 weeks3
Abbreviations
AAV, ANCA-associated vasculitis; AIS, Aggregate Improvement Score; ANCA, anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody; AZA, azathioprine; BVAS, Birmingham Vasculitis Activity Score; CD19, cluster of differentiation 19; CI, confidence interval; CKD, chronic kidney disease; CWS, Cumulative Worsening Score; CYC, cyclophosphamide; eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate; EQ-5D-5L, EuroQoL 5‑dimension 5-level; GC, glucocorticoid; GPA, granulomatosis with polyangiitis; GTI, Glucocorticoid Toxicity Index; IV, intravenous; MCP-1, monocyte chemoattractant protein-1; MPA, microscopic polyangiitis; MPO, myeloperoxidase; NICE, National Institute for Health and Care Excellence; NNT, number-needed-to-treat; PR3, proteinase 3; QoL, quality of life; RTX, rituximab; SD, standard deviation; SF-36, Medical Outcomes Survey Short Form 36; UACR, urine albumin‑to‑creatinine ratio; VAS, Visual Analogue Scale; VDI, Vasculitis Damage Index.
References
- Avacopan Vifor UK SmPC
- NICE (2022). Avacopan for treating severe active granulomatosis with polyangiitis or microscopic polyangiitis. Available at: https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/TA825. Date accessed: May 2025.
- Jayne D, et al. N Engl J Med 2021;384(7):599–609.
- Jayne D, et al. N Engl J Med 2021;384(7):599–609 [Suppl Appendix].
- European Medicines Agency (2021). First-in-class medicine recommended for treatment of rare blood vessel inflammation. Available at: https:// www.ema.europa.eu/en/news/first-class-medicine-recommended-treatment-rareblood-vessel-inflammation. Date accessed: May 2025
- Jayne D, et al. J Am Soc Nephrol 2021;32.
- McDowell P, et al. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract 2020;9(1):336–72.
- Jayne DRW, et al. N Engl J Med 2024;390:388.
UK-AVA-2500007 | Date of preparation: May 2025
Safety, Dosing and Administration
Safety profile of Avacopan Vifor

Most common adverse reactions:1

Nausea
23.5%

Headache
20.5%

Decreased white blood cell count
18.7%

Nasopharyngitis
15.1%

Diarrhoea
15.1%

Vomiting
15.1%

Upper respiratory tract infection
14.5%
The most common serious adverse reactions are liver function abnormalities (5.4%) and pneumonia (4.8%)1
In the post-marketing setting, drug-induced liver injury and vanishing bile duct syndrome (VBDS), including cases with fatal outcome, have been reported (frequency unknown)1
Avacopan Vifor is contraindicated for use in patients hypersensitive to the active substance or any of the excipients1
Avacopan Vifor requires additional monitoring, please see the SmPC for more information
In ADVOCATE, the Avacopan Vifor-based regimen was associated with fewer AEs of any kind, serious AEs, deaths, infections and potentially GC-related AEs vs a GC-based regimen3

Overall subject incidence of SAEs, including vasculitis, was 42.2% in the Avacopan Vifor-based regimen and 45.1% in the GC‑based regimen3
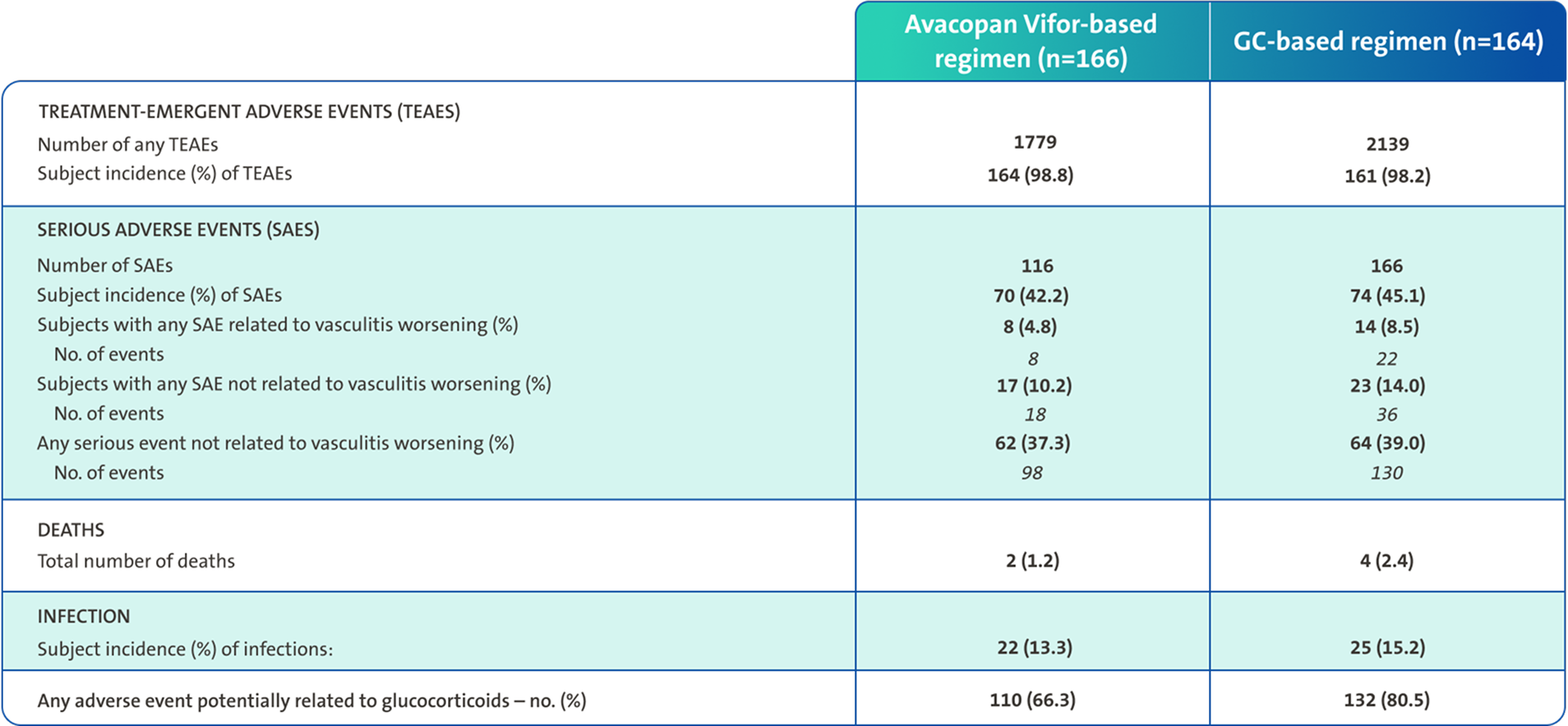
SAEs were defined as any AE that resulted in death, was immediately life-threatening, required or prolonged hospitalisation, resulted in persistent or clinically significant disability or incapacity, was a birth defect, or was an important event that might jeopardise the patient or might have required intervention to prevent any of the above3
Avacopan Vifor is taken as a fixed oral dose, with required monitoring1





If a patient misses a dose, the missed dose is to be taken as soon as possible, unless within three hours of the next scheduled dose. If within three hours, then the missed dose is not to be taken1
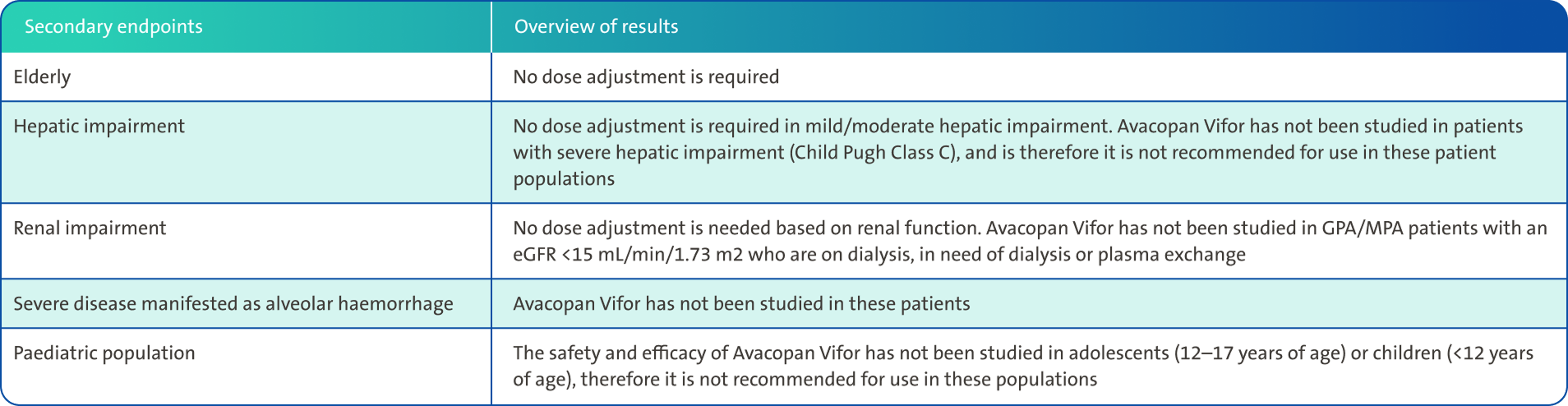
Dose adjustments for special populations1

Special warnings and precautions for use1

Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to the active substance or to any of the excipients
Hepatotoxicity, blood and the immune system1

Avacopan Vifor must be avoided in patients with signs of liver disease, such as elevated AST, ALT, alkaline phosphatase (ALP), or total bilirubin >3 times ULN

Hepatic transaminases, total bilirubin and white blood cell (WBC) count must be obtained prior to initiation of therapy.
Patients must be monitored for:
- Hepatic transaminases and total bilirubin at least every 4 weeks after the start of therapy for the first 6 months of treatment, and as clinically indicated thereafter*
- WBC count as clinically indicated and as part of the routine follow-up of the patient’s underlying condition†

Treatment with Avacopan Vifor must not be initiated if WBC count is less than 3500/μL, or neutrophil count less than 1500/μL, or lymphocyte count less than 500/μL
Please consult the Summary of Product Characteristics for full details on Special Warnings and Precautions
*Treatment must be re-assessed clinically and temporarily stopped if ALT or AST is >3x ULN. Treatment must be temporarily stopped if ALT or AST is >5× ULN. Please consult Summary of Product Characteristics for information about permanent discontinuation.
†Treatment must be temporarily stopped if a patient develops leukopenia (white blood cell count <2×109/L), neutropenia (neutrophils <1×109/L) or lymphopenia (lymphocytes <0.2×109/L).
Immunisations and infections1

The safety of immunisation with live vaccines following Avacopan Vifor therapy has not been studied. Administer vaccinations preferably prior to initiation of treatment with Avacopan Vifor or during quiescent phase of the disease

Patients must be assessed for any serious infections. Avacopan Vifor has not been studied in patients with hepatitis B, hepatitis C, or HIV infections, and therefore caution should be exercised when treating patients with a history of these infections as well as tuberculosis. Treatment must be temporarily stopped if a patient has an active, serious infection (i.e. requiring hospitalisation or prolonged hospitalisation)

Monitor patients treated for ANCA-associated vasculitis according to standard practice for clinical signs and symptoms of Neisseria infections

Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia prophylaxis is recommended for adult GPA/MPA patients during Avacopan Vifor treatment, according to local clinical practice guidelines
Other conditions and treatments1

Angioedema has been reported in patients receiving Avacopan Vifor and Avacopan Vifor must be withheld in cases of angioedema

Avacopan Vifor is a moderate inhibitor of CYP3A4 in vivo and may increase the plasma exposures of concomitant medicinal products that are CYP3A4 substrates. Adjust doses or monitor for adverse effects as per the respective product's Summary of Product Characteristics.
Avacopan Vifor co-administration with simvastatin increased simvastatin exposure significantly. Refer to simvastatin's Summary of Product Characteristics for dose adjustments.

Avacopan Vifor is not recommended for use during pregnancy or in women of child-bearing potential not using contraception.
A decision must be made whether to discontinue breast-feeding or to discontinue/abstain from Avacopan Vifor, taking into account the benefit of breast-feeding for the child and the benefit of an Avacopan Vifor-based regimen for the woman.
There is no data on the effects of Avacopan Vifor on human fertility. Animal data did not indicate any impairment of male or female fertility

AAV and its treatment may be associated with other conditions. Special considerations for the use of Avacopan Vifor in GPA/MPA patients include:
- Patients with GPA or MPA are at risk of cardiac disorders such as myocardial infarction, cardiac failure, and cardiac vasculitis. A treatment regimen based on the combination with cyclophosphamide followed by azathioprine may carry an increased risk for cardiac disorders as compared to a regimen based on the combination with rituximab
- Immunomodulatory medicinal products may increase the risk for malignancies. The clinical data are currently limited
- Avacopan Vifor contains macrogolglycerol hydroxystearate, which may cause stomach upset and diarrhoea
Please consult the Summary of Product Characteristics for full details on Special Warnings and Precautions
References & footnotes
Footnotes
*All the patients received one of three regimens: CYC IV at a dose of 15 mg/kg of body weight up to 1.2 g on Day 1 and at Weeks 2, 4, 7, 10, and 13; CYC orally at a dose of 2 mg/kg up to 200 mg/day for 14 weeks; or IV RTX at a dose of 375 mg/m2 body-surface area/week for 4 weeks. From Week 15 onward, CYC was followed by oral AZA at a target dose of 2 mg/kg/day. No RTX was given beyond the first 4 weeks3
Abbreviations
AAV, ANCA-associated vasculitis; AE, adverse events; ANCA, anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody; ALP, alkaline phosphate; ALT, alanine aminotransferase; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; AZA, azathioprine; CYC, cyclophosphamide; CYP3A4, Cytochrome P450 3A4; eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate; GC, glucocorticoid; GPA, granulomatosis with polyangiitis; HIV, human immunodeficiency virus; MPA, microscopic polyangiitis; RTX, rituximab; SAE, serious adverse event; TEAE, treatment-emergent adverse event; ULN, upper limit of normal; VBDS, vanishing bile duct syndrome; WBC, white blood cell.
References
- Avacopan Vifor UK SmPC.
- NICE (2022). Avacopan for treating severe active granulomatosis with polyangiitis or microscopic polyangiitis. Available at: https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/TA825. Date accessed: May 2025.
- Jayne D, et al. N Engl J Med 2021;384(7):599–609.
UK-AVA-2500012 | Date of preparation: May 2025
Resources







References & footnotes
Abbreviations
AAV, ANCA-associated vasculitis; ANCA, anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody; GPA, granulomatosis with polyangiitis; MPA, microscopic polyangiitis; NICE, National Institute for Health and Care Excellence.
References
- Avacopan Vifor UK SmPC.
- NICE (2022). Avacopan for treating severe active granulomatosis with polyangiitis or microscopic polyangiitis. Available at: https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/TA825. Last accessed: August 2025.
UK-AVA-2500013 | Date of preparation: August 2025
Adverse events should be reported. Reporting forms and information for the United Kingdom can be found at https://yellowcard.mhra.gov.uk/ or search for MHRA Yellow Card in the Google Play or Apple App Store. Adverse events should also be reported to Vifor Fresenius Medical Care Renal Pharma, care of Vifor Pharma Ltd.
Tel: +44 1276 853633. E-mail: MedicalInfo_UK@viforpharma.com.

Stay informed
Register with CSL for the latest releases. This will include promotional content
Register


