VELTASSA®
(patiromer)
Find out more about Veltassa® (patiromer) for the treatment of hyperkalaemia

VELTASSA®
(patiromer)
Find out more about Veltassa® (patiromer) for the treatment of hyperkalaemia
Veltassa® is indicated for the treatment of hyperkalaemia in adults and adolescents aged 12-17 years.1 Please note that the recommended adolescent dosage (4 g once-daily distributed in 1 g sachets) is currently not available. Please refer to the Summary of Product Characteristics for full prescribing information.
Menu
Efficacy & Safety
Efficacy
Hyperkalaemia can be a prevalent and recurrent problem in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) and/or heart failure (HF)2,3
Veltassa significantly reduced K+ levels from the first dose4
Study design
Phase I, open-label, single-arm study
Study objective
Determine Veltassa's onset of action
Study population
- N=25
- eGFR 15 to <90 mL/min/1.73 m2
- Taking at least one RAASi
Primary endpoint
Change in serum K+ from baseline during the 48 hours after the first dose
Secondary endpoint
Change in serum K+ from baseline in prespecified subgroups defined by severity of hyperkalaemia at baseline
Exploratory endpoint
Proportion of patients achieving normokalaemia
The study dose was 8.4 g of Veltassa twice daily.4 The recommended starting dose is 8.4 g Veltassa once daily up to a maximum dose of 25.2 g daily.1 Please always refer to the Veltassa Summary of Product Characteristics for full prescribing details.
Mean change in Serum K+ over 48 hours4
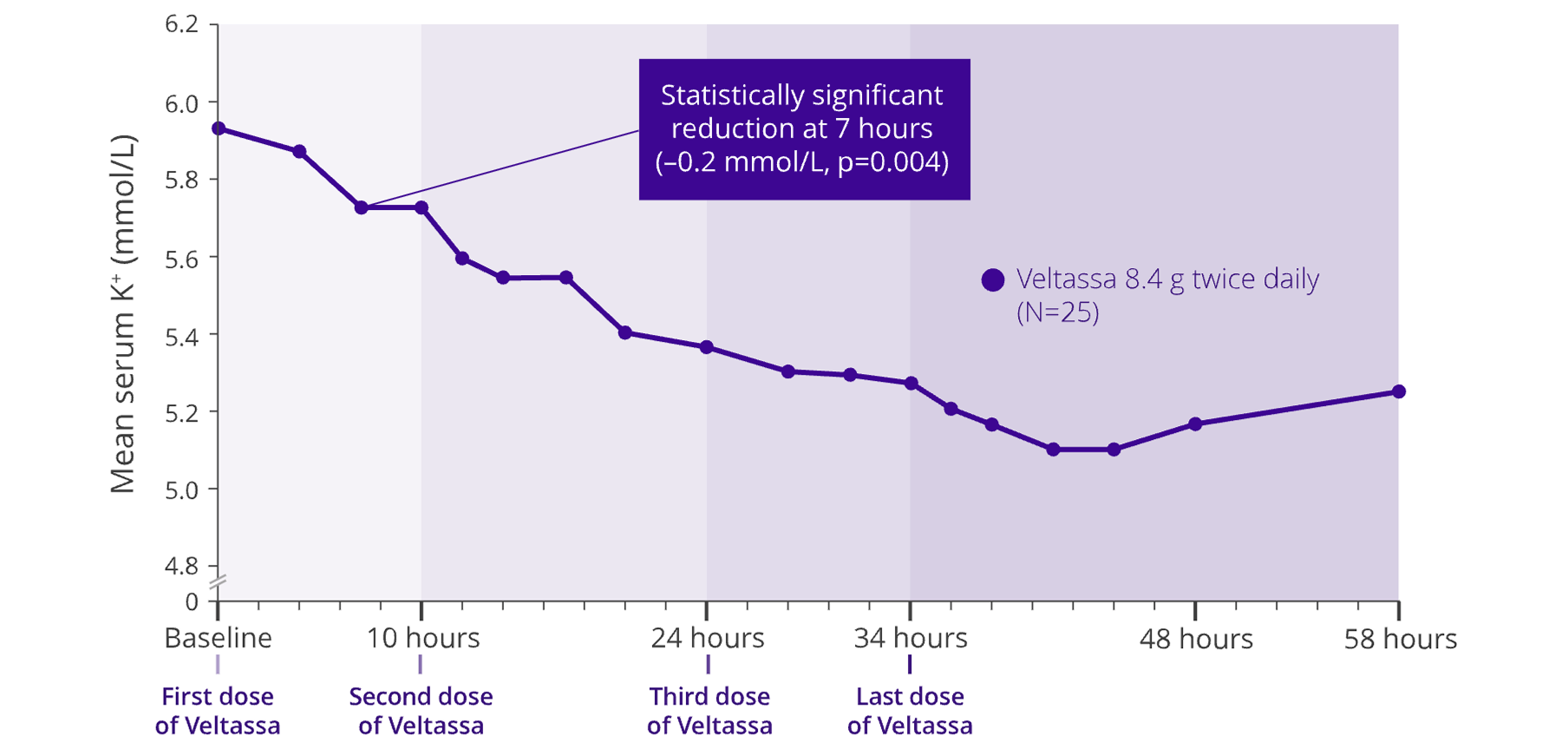
Treatment phase
Adapted from Bushinksky et al. 2015.4
- Serum K+ reduction from baseline in 4 hours (p=NS), and significant (p=0.004) reduction at 7 hours after first dose4
- Serum K+ did not significantly increase for 24 hours after the last dose of Veltassa4
- Veltassa was well tolerated over the treatment period with no serious adverse events reported4
- The most common adverse events were mild constipation and mild hypotension4
Veltassa provided sustained K+ control5
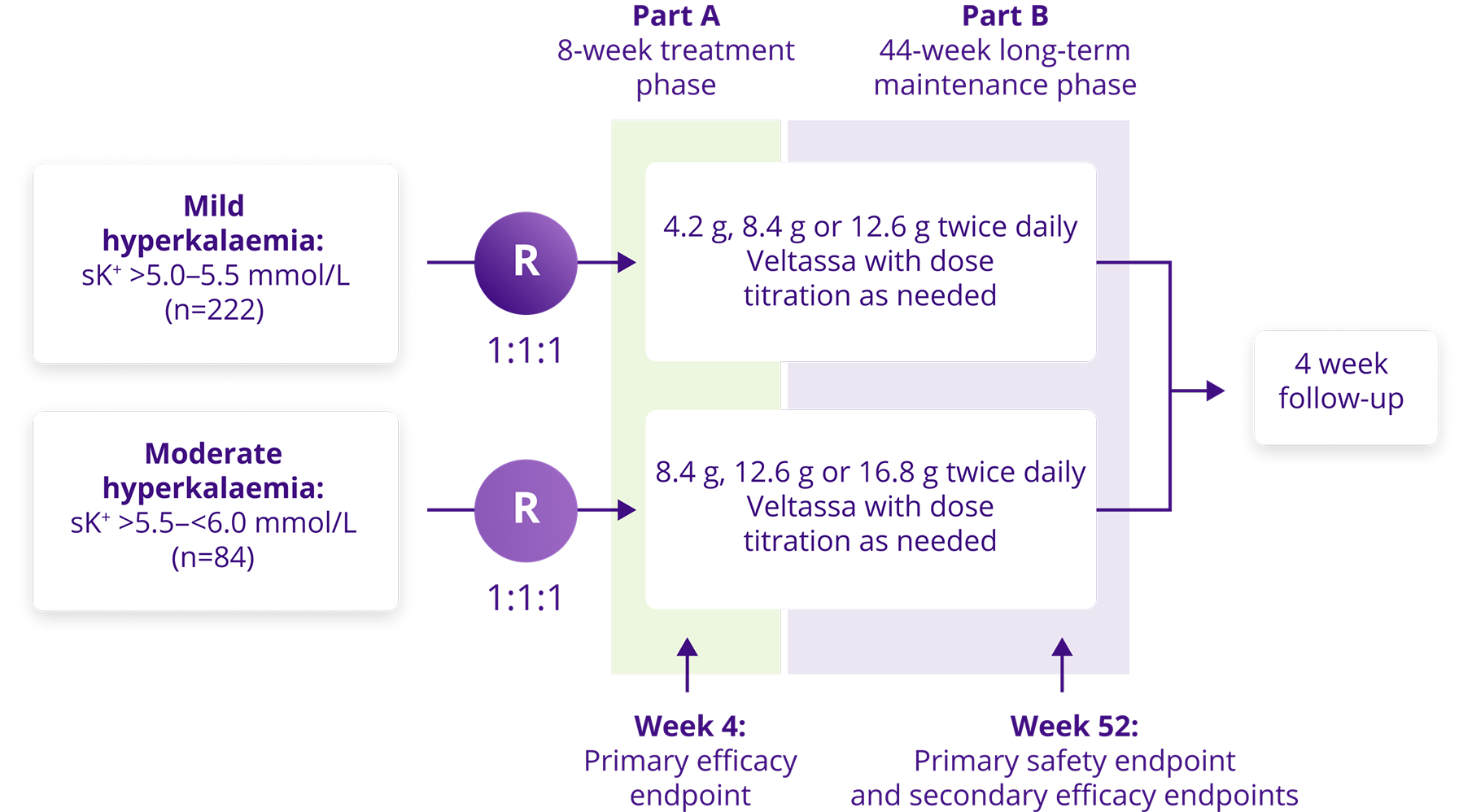
AMETHYST-DN study design5
Study objectives
- Determine the optimal starting dose of Veltassa
- Evaluate the long-term safety and efficacy of Veltassa for the treatment of hyperkalaemia in patients with CKD, T2DM and hypertension
Study population
- N=306
- CKD (eGFR 15 to 60 mL/min/1.73 m2), T2DM, hypertension, stable RAASi dose
- Hyperkalaemia serum K+ >5.0 mmol/L
Primary endpoints
- Mean change in serum K+ level from baseline to week 4 or prior to initiation of dose titration
- Adverse events over 52 weeks
Selected secondary endpoint
- Mean change in serum K+ level over 52 weeks
Study design
- Phase II, multi-centre, open-label, dose-ranging, randomised, 52 weeks
A dose of 33.6 g/day was studied in the trial.5 The recommended starting dose is 8.4 g of Veltassa once daily up to a maximum dose of 25.2 g daily.1 Please always refer to the Veltassa Summary of Product Characteristics for full prescribing details.
Mean change in serum K+ over 1 year5
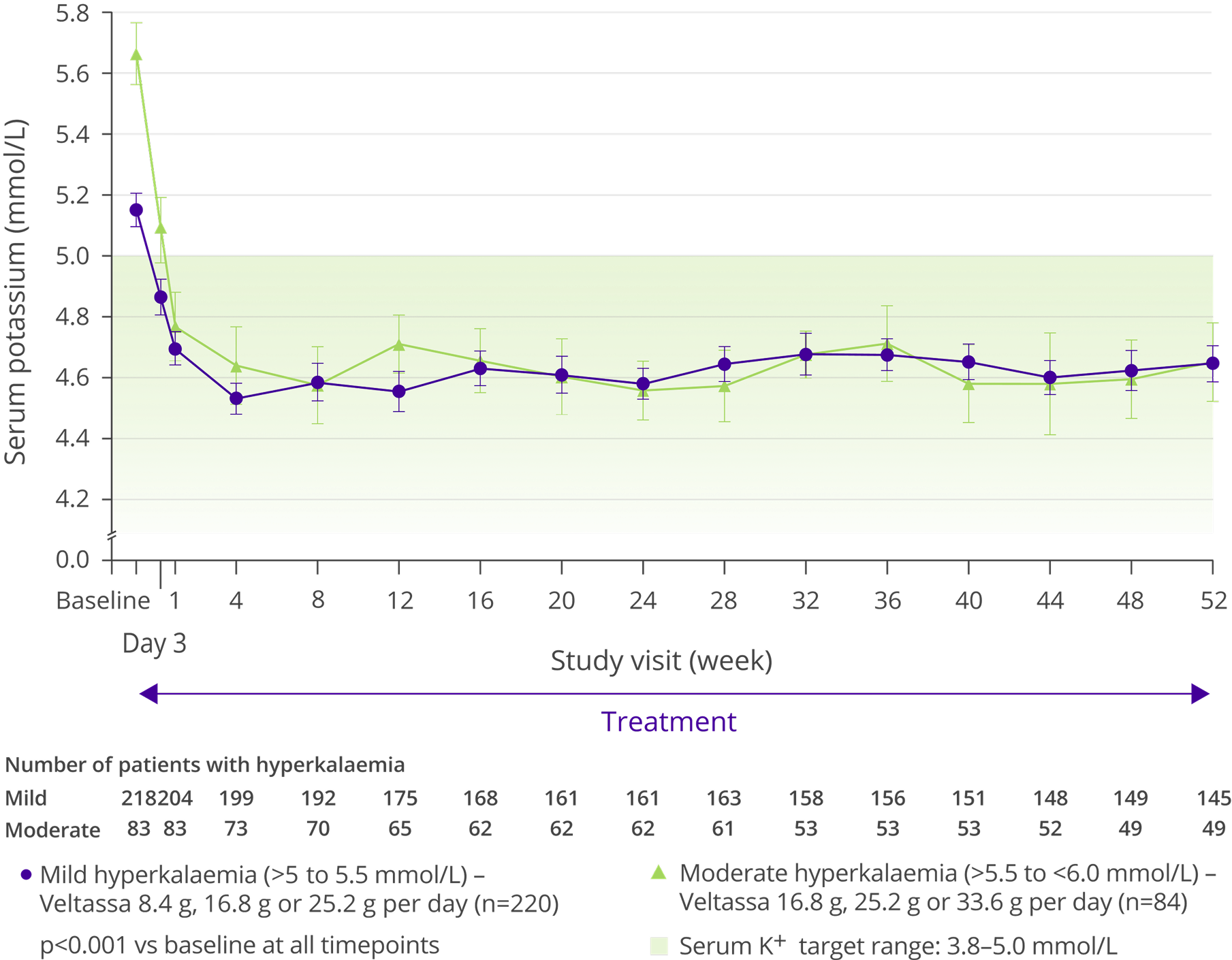
Adapted from Bakris et al, 2015.5
- Over 52 weeks 20% of patients reported an adverse event considered to be related to Veltassa by the investigator5
- The most frequently reported adverse events (≥5% of patients) included worsening of CKD (9.2%), hypomagneseamia (8.6%), worsening of hypertension (7.9%), constipation (6.3%) and diarrhoea (2.7%)5
Mean change in serum K+ after discontinuation of Veltassa at Week 52
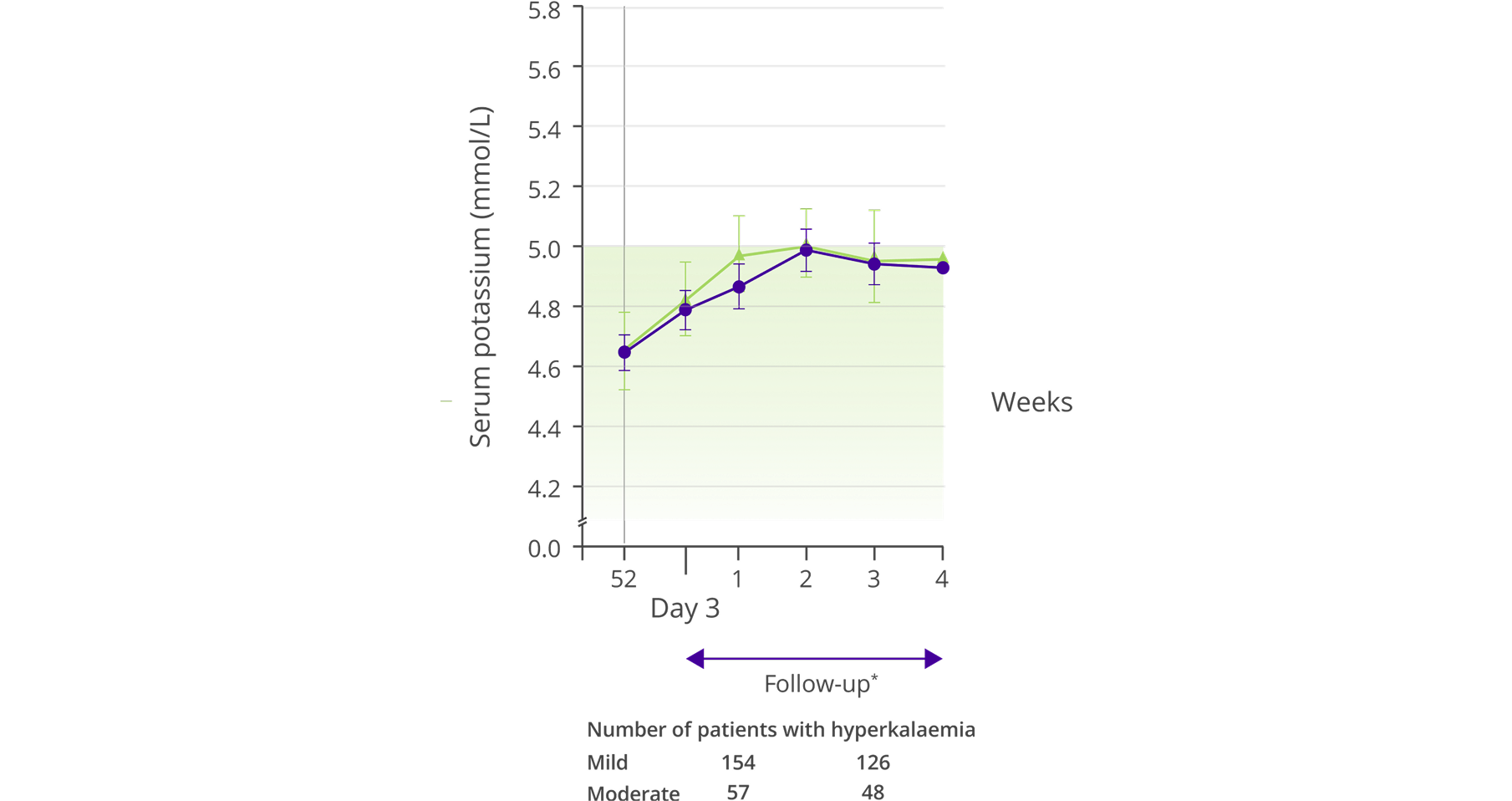
Adapted from Bakris et al, 2015.5
- Over 52 weeks 20% of patients reported an adverse event considered to be related to Veltassa by the investigator5
- The most frequently reported adverse events (≥5% of patients) included worsening of CKD (9.2%), hypomagneseamia (8.6%), worsening of hypertension (7.9%), constipation (6.3%) and diarrhoea (2.7%)5
Veltassa was generally well tolerated in clinical trials1
The most common (≥1/100 to <1/10) adverse reactions observed in clinical studies were mostly mild-to-moderate and generally resolved spontaneously or with treatment:1
Constipation
Hypomagnesaemia*
Diarrhoea
Abdominal pain
Flatulence
Nausea
Vomiting is an uncommon adverse reaction (≥1/1,000 to <1/100).1
*Hypomagnesaemia was mild-to-moderate, with 0.3% of patients developing a serum magnesium level <1 mg/dL (0.4 mmol/L). Serum magnesium should be monitored for at least 1 month after initiating treatment, and magnesium supplementation considered in patients who develop low serum magnesium levels.1
Veltassa is the only K+ binder that enabled RAAS inhibition therapy in placebo-controlled trials6,7
- In patients with CKD and/or HF, elevated serum K+ is one of the principal reasons for non-initiation, down-titration or discontinuation of RAASi therapy3,8
- Mortality risk doubled when RAASi therapy was reduced or stopped for patients with HF8

May enable RAASi therapy6,7

The only K+ binder with once-daily dosing
from the start1
Specifically designed to exchange K+ for Ca2+ 1,9

Suitable for ongoing prescribing in primary care10*
*Initiation must be in specialist care.10
References & footnotes
Abbreviations
Ca2+, calcium; CKD, chronic kidney disease; eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate; HF, heart failure; K+, potassium; NS, not significant; R, randomisation; RAAS, renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system; RAASi, renin‑angiotensin-aldosterone system inhibitor; sK+, serum potassium; T2DM, type 2 diabetes mellitus.
References
- Veltassa® SmPC.
- Dunn JD, et al. Am J Manag Care 2015;21:S307–15.
- Rosano GMC, et al. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Pharmacother 2018;4(3):180–8.
- Bushinsky DA, et al. Kidney Int 2015;88(6):1427–33.
- Bakris GL, et al. JAMA 2015;314(2):151–61.
- Weir MR, et al. N Engl J Med 2015;372(3):211–21.
- Pitt B, et al. Eur Heart J 2011;32:820–8.
- Epstein M, et al. Am J Manag Care 2015;21:S212–20.
- Li L, et al. J Card Pharmacol Ther 2016;21(5):456–65.
- NICE (2020). Patiromer for treating hyperkalaemia. Technology appraisal guidance TA623. Available at: https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ta623. Date accessed: August 2025.
Safety
Veltassa is a next-generation, spherical, non-absorbed polymer, specifically designed to exchange K+ for Ca2+ and not Na+ 1,2
Veltassa is suitable for patients who cannot tolerate even a small increase in Na+ load2
Salt intake requires consideration in:

patients with oedema2

patients with hypertension2

patients with heart failure2
Mode of action
No systemic absorption
- Veltassa's non-absorbed nature may contribute to its safety profile1
Binds K+ in the colon
- Veltassa is specially designed to act in the colon where the concentration of K+ is highest1,2
Veltassa was generally well tolerated in clinical trials1
The most common (≥1/100 to <1/10) adverse reactions observed in clinical studies were mostly mild-to-moderate and generally resolved spontaneously or with treatment:1
Constipation
Hypomagnesaemia*
Diarrhoea
Abdominal pain
Flatulence
Nausea
Vomiting is an uncommon adverse reaction (≥1/1,000 to <1/100).1
*Hypomagnesaemia was mild-to-moderate, with 0.3% of patients developing a serum magnesium level <1 mg/dL (0.4 mmol/L). Serum magnesium should be monitored for at least 1 month after initiating treatment, and magnesium supplementation considered in patients who develop low serum magnesium levels.1
Veltassa has few known drug-drug interactions1
Veltassa has the potential to bind some oral co-administered drugs, which could decrease their gastrointestinal absorption. Increased bioavailability of co-administrated drugs was not observed in the conducted drug-drug interaction studies.1

Concomitant administration in patients using Veltassa showed reduced bioavailability of only three drugs:1,3
- Ciprofloxacin
- Levothyroxine
- Metformin*
There was no interaction when Veltassa and these medicinal products were taken 3 hours apart.1
As precautionary measure, administration of Veltassa should be separated by at least 3 hours from other oral drugs.1
Refer to the Summary of Product Characteristics for the full list of drug-drug interactions.
*Effect of concomitant administration of Veltassa with metformin is similar to taking metformin with food.3
Monitoring and precautions for use1
Serum K+ should be monitored when clinically indicated, including after changes are made to medicinal products that affect the serum K+ concentration and after the Veltassa dose is titrated. Since excessive doses of Veltassa may results in hypokalaemia, serum K+ levels should be monitored when initiated and uptitrated. If it is determined that medical intervention is required, appropriate measures to restore serum K+ may be considered.1

Serum Mg2+ should be monitored for at least 1 month after initiating treatment, and Mg2+ supplementation considered in patients who develop low serum Mg2+ levels.1

Veltassa partially releases Ca2+ some of which may be absorbed. The benefits and risks of administering this medicinal product should be carefully evaluated in patients at risk of hypercalcaemia.1 Serum calcium should be monitored for at least 1 month after initiating treatment and as clinically indicated during treatment.1
Veltassa contains sorbitol as part of the counterion complex. Patients with rare hereditary problems of fructose intolerance should not take this medicine.1

When discontinuing Veltassa, serum potassium levels may rise, especially if RAASi treatment is continued. Patients should be instructed not to discontinue therapy without consulting their physicians. Increases in serum potassium may occur as early as 2 days after the last Veltassa dose.1

Gastrointestinal ischaemia, necrosis and/or intestinal perforation have been reported with other potassium binders. The benefits and risks of administering Veltassa should be carefully evaluated in adult and paediatric patients with current or history of severe gastrointestinal disorders, before and during the treatment.1
Learn more about how Veltassa reduces K+ from the first dose4 and provides sustained long-term control5

May enable RAASi therapy6,7

The only K+ binder with once-daily dosing
from the start1
Specifically designed to exchange K+ for Ca2+ 1,2

Suitable for ongoing prescribing in primary care8*
*Initiation must be in specialist care.8
References & footnotes
Abbreviations
Ca2+, calcium; K+, potassium; Mg2+, magnesium; Na+, sodium; RAAS, renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system; RAASi, renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system inhibitor.
References
- Veltassa® SmPC.
- Li L, et al. J Card Pharmacol Ther 2016;21(5):456–65.
- Lesko LJ, et al. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol Ther 2017;22(5):434–46.
- Bushinsky DA, et al. Kidney Int 2015;88(6):1427–33.
- Bakris GL, et al. JAMA 2015;314(2):151–61.
- Weir MR, et al. N Engl J Med 2015;372(3):211–21.
- Pitt B, et al. Eur Heart J 2011;32:820–8.
- NICE (2020). Patiromer for treating hyperkalaemia. Technology appraisal guidance TA623. Available at: https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ta623. Date accessed: August 2025.
Once-daily dosing
Veltassa is the only K+ binder with once-daily dosing from the start1
Key learning points
- The recommended starting dose for adults is 8.4 g Veltassa once daily1
- The daily dose may be adjusted in intervals of one week or longer, based on the serum potassium level and the desired target range. The daily dose for adults may be increased or decreased by 8.4 g as necessary to reach the desired target range, up to a maximum dose of 25.2 g daily1
- Veltassa can be stored at room temperature for up to 6 months,1 saving space in the fridge
Veltassa should be taken orally. It should be mixed with water and stirred to a suspension of uniform consistency.1
How to take Veltassa in 3 steps1

1. Mix
The required number of sachets of Veltassa should be added to 40 mL (3 tablespoons) of water and stirred well.
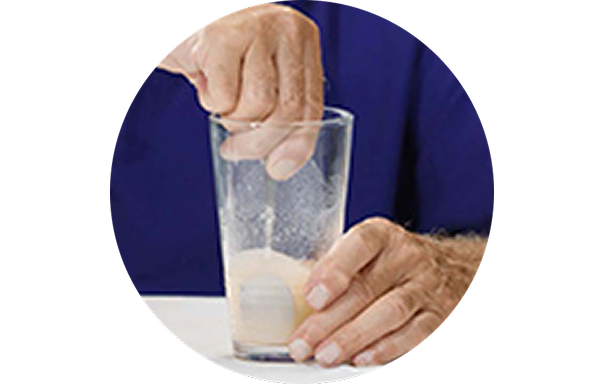
2. Add
Another 40 mL of water should be added and the mixture stirred again. More water can be added if the mixture is too thick.
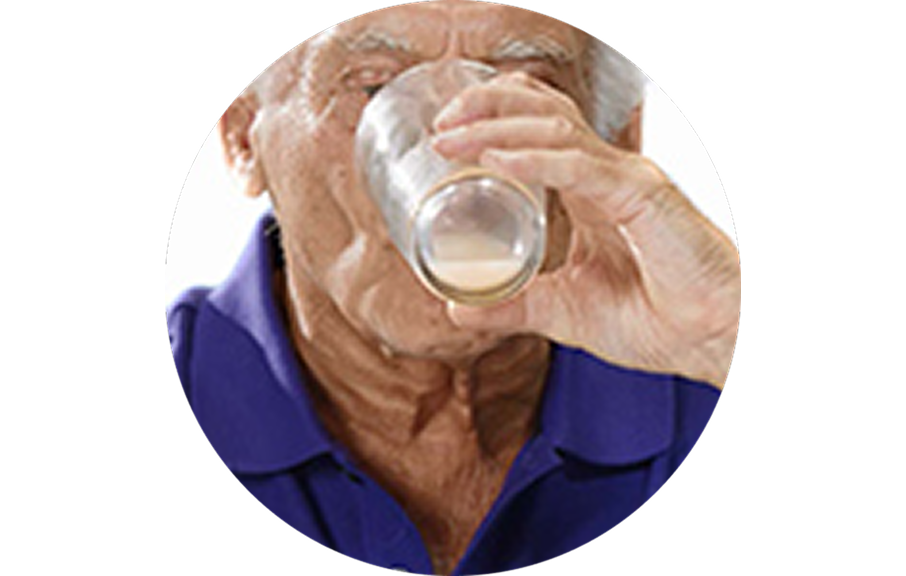

3. Drink
The mixture should be consumed immediately, within 1 hour. If powder remains in the glass, more water can be added to ensure the entire dose is taken.
- Veltassa can be suspended in other drinks such as apple juice, cranberry juice, pineapple juice, orange juice, grape juice, pear juice, apricot nectar, peach nectar, yoghurt, milk, thickener (for example: cornstarch), apple sauce, vanilla and chocolate pudding for added flavour. Cranberry juice should be limited to <400 mL a day as it can affect other medication1
- Veltassa can be taken with or without food1
- Administration of Veltassa should be separated by at least 3 hours from other oral medicinal products1
- In a palatability study of 62 subjects, ~90% of patients found Veltassa to be a positive experience in terms of odour or taste2
Storage information
- Veltassa can be kept at room temperature (below 25°C) for use within 6 months, after storage and transportation at 2°C–8°C1
- Veltassa must be stored and transported refrigerated (2°C–8°C).1 The shelf life of Veltassa is 3 years1
- Store Veltassa at room temperature (below 25°C) for use within 6 months once removed from the refrigerator1
FOR HOSPITAL USE
Veltassa can be dispensed from the pharmacy to other wards, where it can be stored at room temperature and used within 6 months. This change will save space in the hospital fridge.1
FOR COMMUNITY USE
After collecting Veltassa from their local pharmacy, where it has been refrigerated, patients can store Veltassa at room temperature and use it within 6 months.1

May enable RAASi therapy3,4

The only K+ binder with once-daily dosing
from the start1

Specifically designed to exchange K+ for Ca2+ 1,5

Suitable for ongoing prescribing in primary care6*
*Initiation must be in specialist care.6
References & footnotes
Abbreviations
Ca2+, calcium; K+, potassium; RAAS, renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system; RAASi, renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system inhibitor.
References
- Veltassa® SmPC.
- Brenner M, et al. Poster P4-075, American Society of Health System Pharmacists Annual Meeting. Las Vegas, NV.
- Weir MR, et al. N Engl J Med 2015;372(3):211–21.
- Pitt B, et al. Eur Heart J 2011;32(7):820–8.
- Li L, et al. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol Ther 2016;21(5):456–65.
- NICE (2020). Patiromer for treating hyperkalaemia. Technology appraisal guidance TA623. Available at: https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ta623. Date accessed: August 2025.
FAQs
Veltassa Frequently Asked Questions
What do the guidelines recommend?
In recent years, major guidelines such as NICE, SMC, UK Renal Association, ESC and KDIGO have updated their guidance to include the use of next-generation potassium binders to manage persistent hyperkalaemia.2–7
NICE technology appraisal guidance 623, 20202
Veltassa is recommended as an option for treating hyperkalaemia in adults only if used:
- in emergency care for acute life-threatening hyperkalaemia alongside standard care or
- for people with persistent hyperkalaemia and stages 3b to 5 chronic kidney disease (CKD) or heart failure, if they:
- have a confirmed serum K+ level of at least 6.0 mmol/L and
- are not taking, or are taking a reduced dosage of, a RAAS inhibitor because of hyperkalaemia and
- are not on dialysis.
Stop Veltassa if RAAS inhibitors are no longer suitable.
SMC guidance number 2381, 20213
Veltassa is accepted for restricted use within NHSScotland and indicated for the treatment of hyperkalaemia in adults.
SMC restriction: patients with hyperkalaemia (defined as a serum K+ of >6.0 mmol/L) with CKD stage 3b to 5 and/or heart failure, who would otherwise need to down-titrate or discontinue their RAASi therapy to maintain a clinically acceptable serum K+ level (normokalaemia).
Veltassa sorbitex calcium offers an additional treatment choice in the therapeutic class of non-absorbed cation-exchange compounds that act as selective K+ binders.
SMC guidance number 2568, 20234
Veltassa is accepted for restricted use within NHSScotland and indicated for the treatment of hyperkalaemia in adults.
SMC restriction: in the emergency care setting for the treatment of acute, life-threatening hyperkalaemia alongside standard care. Veltassa sorbitex calcium offers an additional treatment choice in the therapeutic class of non-absorbed cation-exchange compounds that act as K+ binders.
UK Renal Association, 20205
We recommend that Veltassa is an option in the management of persistent hyperkalaemia with a confirmed serum K+
≥6.0 mmol/L in outpatients with CKD Stage 3b–5 (not on dialysis) or heart failure receiving a suboptimal dose or not receiving RAASi therapy due to hyperkalaemia.
2021 ESC guidelines for the management of hyperkalaemia in patients with heart failure6
The guidelines include recommendations for treatment of most non-cardiovascular comorbidities, including hyperkalaemia. Administration of K+-lowering agents may allow initiation or up-titration of RAASi therapy in a larger proportion of patients.
KDIGO 2024 guidance for the use of RAAS inhibitors in patients with CKD7
The guideline includes practice points on how to optimise and maintain RAASi treatment for patients with CKD.
What are the storage considerations for Veltassa?
Store and transport refrigerated (2°C– 8°C).1
If stored at room temperature (below 25°C), Veltassa should be used within 6 months of being taken out of the refrigerator.1
For either storage condition, Veltassa should not be used after the expiry date printed on the sachet.1
The mixture should be taken within 1 hour of initial suspension.1
FOR HOSPITAL USE
Veltassa can be dispensed from the pharmacy to other wards, where it can be stored at room temperature and used within 6 months. This change will save space in the hospital fridge.1
FOR COMMUNITY USE
After collecting Veltassa from their local pharmacy, where it has been refrigerated, patients can store Veltassa at room temperature and use it within 6 months.1
Please refer to the Summary of Product Characteristics for further information.
What is the recommended dosing of Veltassa?
Veltassa is indicated for the treatment of hyperkalaemia in adults and adolescents aged 12–17 years.1
Dosing
The recommended starting dose for adults is 8.4 g Veltassa once daily.1
The daily dose may be adjusted in intervals of 1 week or longer, based on the serum K+ level and the desired target range. The daily dose for adults may be increased or decreased by 8.4 g as necessary to reach the desired target range, up to a maximum dose of 25.2 g daily.1
Please note that the recommended adolescent dosage (4 g once daily distributed in 1 g sachets) is currently not available.
More information about the dosing of VeltassaPlease refer to the Summary of Product Characteristics for further details about dosing and administration.
How is Veltassa administered?
Veltassa is indicated for the treatment of hyperkalaemia in adults and adolescents aged 12–17 years.1
Administration
Veltassa should be taken orally. It should be mixed with water and stirred to a suspension of uniform consistency.1
Veltassa can be suspended in other drinks such as apple juice, cranberry juice, pineapple juice, orange juice, grape juice, pear juice, apricot nectar, peach nectar, yoghurt, milk, thickener (for example: cornstarch), apple sauce, vanilla and chocolate pudding for added flavour. Cranberry juice should be limited to <400 mL a day as it can affect other medication.1
Administration of Veltassa should be separated by 3 hours from other oral medicinal products.1
More information about the administration of VeltassaPlease refer to the Summary of Product Characteristics for further details about dosing and administration.
How long does it take for the onset of action?
The onset of action of Veltassa occurs 4–7 hours after administration:1
- Serum K+ reduction occurs in 4 hours (p=NS) and significant reduction at 7 hours (p=0.004) after first dose, versus baseline8
Veltassa should not replace emergency treatment for life‑threatening hyperkalaemia.1
More information about the efficacy of VeltassaHow was Veltassa tolerated in clinical trials?
The majority of the adverse reactions (ARs) were hypomagnesaemia (1.8%) and gastrointestinal disorders, with the most frequently reported ARs being constipation (3.7%), diarrhoea (3%), abdominal pain (1.4%), nausea (1.3%) and flatulence (1%).1
Gastrointestinal disorder reactions were generally mild to moderate in nature, did not appear to be dose related and generally resolved spontaneously or with treatment.1
Hypomagnesaemia was mild to moderate, with 0.3% of patients developing a serum magnesium level <1 mg/dL (0.4 mmol/L).1
Are there any special warnings and precautions for use associated with Veltassa?
- The benefits and risks of administering Veltassa should be carefully evaluated in adult and paediatric patients with current or history of severe gastrointestinal disorders, before and during the treatment.1
- Serum K+ should be monitored when clinically indicated, including after changes are made to medicinal products that affect the serum K+ concentration and after the Veltassa dose is titrated. Since excessive doses of Veltassa may result in hypokalaemia, serum K+ levels should be monitored when initiated and uptitrated. If it is determined that medical intervention is required, appropriate measures to restore serum K+ may be considered.1
- Serum Mg2+ should be monitored for at least 1 month after initiating treatment and Mg2+ supplementation considered in patients who develop low serum Mg2+ levels.1
- Veltassa partially releases Ca2+, some of which may be absorbed. The benefits and risks of administering this medicinal product should be carefully evaluated in patients at risk of hypercalcaemia.1 Serum calcium should be monitored for at least 1 month after initiating treatment and as clinically indicated during treatment.1
- Veltassa contains sorbitol as part of the counterion complex. Patients with rare hereditary problems of fructose intolerance should not take this medicine.1
- When discontinuing Veltassa, serum K+ levels may rise, especially if RAASi treatment is continued. Patients should be instructed not to discontinue therapy without consulting their physicians. Increases in serum K+ may occur as early as 2 days after the last Veltassa dose.1
- Gastrointestinal ischaemia, necrosis and/or intestinal perforation have been reported with mother potassium binders. The benefits and risks of administering Veltassa should be carefully evaluated in adult and paediatric patients with current or history of severe gastrointestinal disorders, before and during the treatment.1
Please refer to the Summary of Product Characteristics for a full list of special warnings and precautions.
What should be considered when taking other medications with Veltassa?
Administration of Veltassa should be separated by 3 hours from other oral medicinal products.1
Veltassa has the potential to bind some oral co-administered drugs, which could decrease their gastrointestinal absorption. Increased bioavailability of co-administrated drugs was not observed in the conducted drug-drug interaction studies.1
Concomitant administration in patients using Veltassa showed reduced bioavailability of three drugs:1
- Ciprofloxacin
- Levothyroxine
- Metformin
There was no interaction when Veltassa and these medicinal products were taken 3 hours apart.1
Please refer to the Summary of Product Characteristics for the full list of drug-drug interactions.
References & footnotes
Footnotes
AR, adverse reactions; Ca2+, calcium; CKD, chronic kidney disease; ESC, European Society of Cardiology; K+, potassium; KDIGO, Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes; Mg2+, magnesium; NICE, National Institute for Health and Care Excellence; NS, not significant; RAAS, renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system; RAASi, renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system inhibitor; SMC, Scottish Medicines Consortium.
References
- Veltassa® SmPC.
- NICE (2020). Patiromer for treating hyperkalaemia. Technology appraisal guidance TA623. Available at: https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ta623. Date accessed: August 2025.
- SMC (2021). SMC2381 Patiromer (Veltassa®). Available at: https://www.scottishmedicines.org.uk/media/6179/patiromer-veltassa-abbreviated-final-july-2021-for-website.pdf. Date Accessed: August 2025.
- SMC (2021). SMC2568 Patiromer sorbitex calcium 8.4 mg and 16.8 mg powder for oral suspension (Veltassa®). Available at: https://scottishmedicines.org.uk/media/7508/patiromer-veltassa-abbreviated-final-May-2023-amended-040423-for-website.pdf. Date Accessed: August 2025.
- UK Renal Association (2025). Clinical practice guidelines - treatment of acute hyperkalaemia in adults. Available at: https://ukkidney.org/sites/renal.org/files/RENAL%20ASSOCIATION%20HYPERKALAEMIA%20GUIDELINE%20-%20JULY%202022%20V2_0.pdf. Date accessed: August 2025.
- McDonagh TA, et al. Eur Hear J 2021;42:3599–726. (+ Suppl).
- KDIGO 2021 Clinical Practice Guideline for the Management of Blood Pressure in Chronic Kidney Disease. Kidney Int 2024;105:S117–S314.
- Bushinsky DA, et al. Kidney Int 2015;88(6):1427–33.
Efficacy
Hyperkalaemia can be a prevalent and recurrent problem in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) and/or heart failure (HF)2,3
Veltassa significantly reduced K+ levels from the first dose4
Study design
Phase I, open-label, single-arm study
Study objective
Determine Veltassa's onset of action
Study population
- N=25
- eGFR 15 to <90 mL/min/1.73 m2
- Taking at least one RAASi
Primary endpoint
Change in serum K+ from baseline during the 48 hours after the first dose
Secondary endpoint
Change in serum K+ from baseline in prespecified subgroups defined by severity of hyperkalaemia at baseline
Exploratory endpoint
Proportion of patients achieving normokalaemia
The study dose was 8.4 g of Veltassa twice daily.4 The recommended starting dose is 8.4 g Veltassa once daily up to a maximum dose of 25.2 g daily.1 Please always refer to the Veltassa Summary of Product Characteristics for full prescribing details.
Mean change in Serum K+ over 48 hours4

Treatment phase
Adapted from Bushinksky et al. 2015.4
- Serum K+ reduction from baseline in 4 hours (p=NS), and significant (p=0.004) reduction at 7 hours after first dose4
- Serum K+ did not significantly increase for 24 hours after the last dose of Veltassa4
- Veltassa was well tolerated over the treatment period with no serious adverse events reported4
- The most common adverse events were mild constipation and mild hypotension4
Veltassa provided sustained K+ control5
AMETHYST-DN study design5
Study objectives
- Determine the optimal starting dose of Veltassa
- Evaluate the long-term safety and efficacy of Veltassa for the treatment of hyperkalaemia in patients with CKD, T2DM and hypertension
Study population
- N=306
- CKD (eGFR 15 to 60 mL/min/1.73 m2), T2DM, hypertension, stable RAASi dose
- Hyperkalaemia serum K+ >5.0 mmol/L
Primary endpoints
- Mean change in serum K+ level from baseline to week 4 or prior to initiation of dose titration
- Adverse events over 52 weeks
Selected secondary endpoint
- Mean change in serum K+ level over 52 weeks
Study design
- Phase II, multi-centre, open-label, dose-ranging, randomised, 52 weeks

A dose of 33.6 g/day was studied in the trial.5 The recommended starting dose is 8.4 g of Veltassa once daily up to a maximum dose of 25.2 g daily.1 Please always refer to the Veltassa Summary of Product Characteristics for full prescribing details.
Mean change in serum K+ over 1 year5

Adapted from Bakris et al, 2015.5
- Over 52 weeks 20% of patients reported an adverse event considered to be related to Veltassa by the investigator5
- The most frequently reported adverse events (≥5% of patients) included worsening of CKD (9.2%), hypomagneseamia (8.6%), worsening of hypertension (7.9%), constipation (6.3%) and diarrhoea (2.7%)5
Mean change in serum K+ after discontinuation of Veltassa at Week 52

Adapted from Bakris et al, 2015.5
- Over 52 weeks 20% of patients reported an adverse event considered to be related to Veltassa by the investigator5
- The most frequently reported adverse events (≥5% of patients) included worsening of CKD (9.2%), hypomagneseamia (8.6%), worsening of hypertension (7.9%), constipation (6.3%) and diarrhoea (2.7%)5
Veltassa was generally well tolerated in clinical trials1
The most common (≥1/100 to <1/10) adverse reactions observed in clinical studies were mostly mild-to-moderate and generally resolved spontaneously or with treatment:1
Constipation
Hypomagnesaemia*
Diarrhoea
Abdominal pain
Flatulence
Nausea
Vomiting is an uncommon adverse reaction (≥1/1,000 to <1/100).1
*Hypomagnesaemia was mild-to-moderate, with 0.3% of patients developing a serum magnesium level <1 mg/dL (0.4 mmol/L). Serum magnesium should be monitored for at least 1 month after initiating treatment, and magnesium supplementation considered in patients who develop low serum magnesium levels.1
Veltassa is the only K+ binder that enabled RAAS inhibition therapy in placebo-controlled trials6,7
- In patients with CKD and/or HF, elevated serum K+ is one of the principal reasons for non-initiation, down-titration or discontinuation of RAASi therapy3,8
- Mortality risk doubled when RAASi therapy was reduced or stopped for patients with HF8

May enable RAASi therapy6,7

The only K+ binder with once-daily dosing
from the start1

Specifically designed to exchange K+ for Ca2+ 1,9

Suitable for ongoing prescribing in primary care10*
*Initiation must be in specialist care.10
References & footnotes
Abbreviations
Ca2+, calcium; CKD, chronic kidney disease; eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate; HF, heart failure; K+, potassium; NS, not significant; R, randomisation; RAAS, renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system; RAASi, renin‑angiotensin-aldosterone system inhibitor; sK+, serum potassium; T2DM, type 2 diabetes mellitus.
References
- Veltassa® SmPC.
- Dunn JD, et al. Am J Manag Care 2015;21:S307–15.
- Rosano GMC, et al. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Pharmacother 2018;4(3):180–8.
- Bushinsky DA, et al. Kidney Int 2015;88(6):1427–33.
- Bakris GL, et al. JAMA 2015;314(2):151–61.
- Weir MR, et al. N Engl J Med 2015;372(3):211–21.
- Pitt B, et al. Eur Heart J 2011;32:820–8.
- Epstein M, et al. Am J Manag Care 2015;21:S212–20.
- Li L, et al. J Card Pharmacol Ther 2016;21(5):456–65.
- NICE (2020). Patiromer for treating hyperkalaemia. Technology appraisal guidance TA623. Available at: https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ta623. Date accessed: August 2025.
UK-PAT-2500008 | August 2025
UK-PAT-2500009 | August 2025
UK-PAT-2500010 | August 2025
UK-PAT-2500011 | August 2025
Adverse events should be reported. Reporting forms and information for the United Kingdom can be found at https://yellowcard.mhra.gov.uk/ or search for MHRA Yellow Card in the Google Play or Apple App Store. Adverse events should also be reported to Vifor Fresenius Medical Care Renal Pharma, care of Vifor Pharma Ltd.
Tel: +44 1276 853633. E-mail: MedicalInfo_UK@viforpharma.com.

Stay informed
Register with Vifor Pharma for the latest
releases. This will include promotional content



